Author: |
Ultraviolet organic light-emitting devices (UVOLEDs) are expected to develop into compact, environmentally friendly and large-size ultraviolet light source applications in analysis, information storage, display, biomedical, etc. However, most of the UV emitted organic materials have broad emission spectra, and thus the electroluminescence (EL) spectra of the most reported UVOLEDs have non-ignorable visible light components, which limits the application prospect of UVOLEDs more or less.
Therefore, the development of narrow band pure UV emission OLED with considerable irradiance and satisfactory durability to overcome the bottleneck of practical applications is still a challenge.
In a study published in ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, a research group led by Prof. LIU Xingyuan from Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a high color purity OLED by introducing simple optical structures.
The microcavity UVOLEDs (μC UVOLEDs) were constructed by an asymmetric structural design with a specific distributed bragg reflector (DBR) structure.
The researchers found that the asymmetric microcavity structure can effectively suppress the visible light component, thereby affording narrow-band pure UV emission with tunable wavelength from 366 nm to 400 nm and full width at half maximum (FWHM) of from 9.95 to15.2 nm.
Besides, compared with the reported results, these μCUVOLEDs show orders of magnitude improvement both in irradiance and lifetime owing to the enhenced carrier injection and precise regulation of exciton recombination region in ultrathin microcavity, which can be used to identify the authenticity of RMB.
The improved optoelectronic performance of the μC UVOLEDs indicates that the microcavity effect is useful in achieving the desired narrow peak emission and asymmetric structural design also play an important role in improving the overall performances. This study not only demonstrates the prototype of μC UVOLEDs for portable compact UV sources but also provides a feasible strategy for the optimal design of narrow band pure UVOLEDs by utilizing simple optical structure.
Contact:
Auther: Prof. LIN Jie
Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Changchun, jilin 130033, China
E-mail: linj@ciomp.ac.cn
Article links: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.9b20212
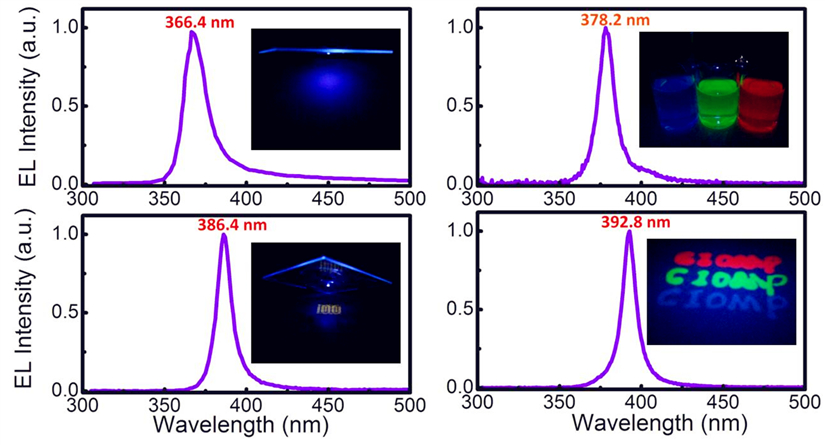
Wavelength tunable μC UVOLEDs with asymmetric structural design (Image by Prof. LIU’s group)
