Author: |
Editor: Srinivasa Rao Konda | Oct 25, 2021
High harmonic generation (HHG) from gases, solids, and laser-induced plasma plumes (LIPs) have attracted researchers' great attention due to their application in attosecond physics and nonlinear spectroscopy. The harmonics intensities and cut-off were significantly affected by different materials.
Recently, Dr. Srinivasa Rao Konda and Prof. LI Wei from the GPL, State Key Laboratory of Applied Optics, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics, and Physics (CIOMP), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborated with Dr. Murali Banovath, Solar Cells and Photonics Research Laboratory, School of Chemistry, University of Hyderabad, India and obtained perovskites 2D nanocrystals for HHG studies. This paper was published in ACS Appl. Nano Mater.
In this work, we have shown the enhancement of higher-order harmonics from intentionally designed two-dimensional (2D) nanocrystals. The synthesis and exploration of adaptable 2D nanocrystals with excellent third-order nonlinear (NLO) properties are applied in various photonic applications. At present, we have demonstrated the efficient HHG from the LIPs of CsPbBr3 and Ni-doped CsPbBr3 nanocrystals. The plasma plumes were produced by ablating the sample targets using ns and ps pulses.
The present work has been focused on the extrication role of Ni dopants in the release of intense harmonics from the plasma plumes using 800 nm as a driving laser beam. The tendency observed in the harmonic intensity development is comparable to the growth in NLO properties (i.e., n2) of the same nanocrystals measured at a similar wavelength.
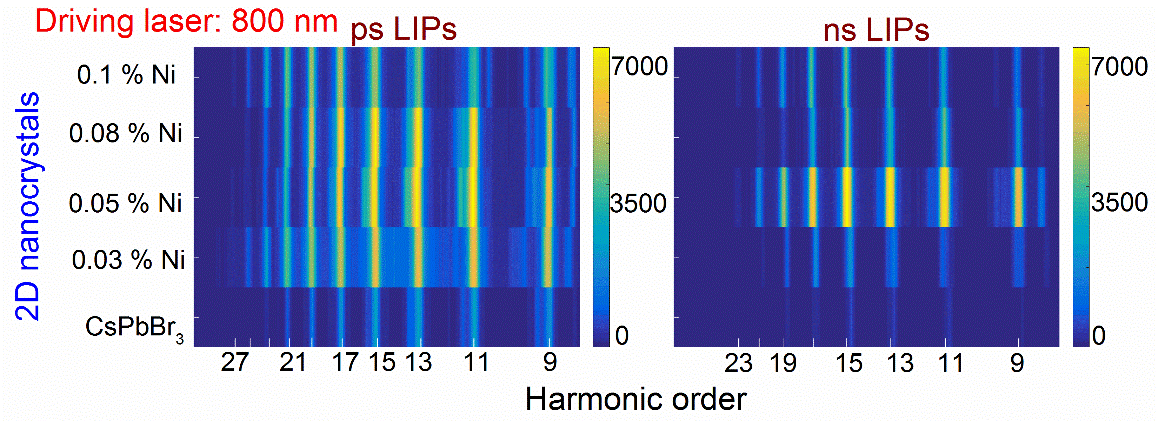
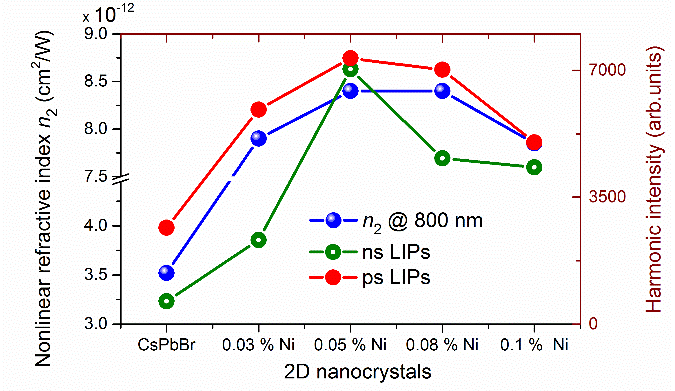
Fig.1 & 2 HHG spectra of 2D nanocrystals plasma plumes ablated by ns and ps pulses and compare harmonic intensity with nonlinear refractive index (Images by Konda).
In the meantime, Dr. Srinivasa Rao Konda, Dr. LAI Yuhang and Prof. LI Wei have shown the advantages of shorter pulse duration, i.e., fs pulses to create the plasma plumes from silver and extend the harmonics cut-off up to 65 order using 800 nm, 35fs pulses as driving laser beam for the first time.The work is published in two articles which are (1) J. Appl. Phys; and (2) Optics & Laser Technology.
Among the several metals, the silver plasma plume is one of the main bases for HHG. The ns, ps, and fs laser pulses were used to produce the silver plasma and revealed that shorter pulse duration leads to enhanced plasma density. For ns, and ps pulses, the plasma extension angle could be lesser with narrower angular distribution of ions than the ns/ps LIPs. Therefore, fs LIPs has higher density than ps and ns LIPs.
Besides, the contribution of Ag atoms was theoretically calculated, Ag+ and Ag2+ towards the generation of HHG. In case of fs LIPs, the calculated theoretical harmonic is closely matched with experiemtnal cut-off, which reveals the advantage of selection of fs laser pulses to create the plasma plumes.
Moreover, the harmonic spectra of silver bulk and nanoparticles were measured by using negatively(-) and positively(+)chirped 135 fs driving pulses. The -ve and + ve chirp pulses lead to blue and red shifts of the harmonic's spectra.
The obtained results showed that Ag is one of the projecting resources for emission of higher-order harmonics. The intensity and cut-off of harmonics could be preciously tuned with respect to driving and heating pulse durations and intensities.
Specifically, the current investigation paid attention to choosing the fs pulses as driving and ablating pulses for improving the intensity and cut-off of harmonics from silver plasma.

Fig.3 HHG spectra of silver bulk and nanoparticles plasma plumes produced by ns, ps, and fs laser pulses(Images by Konda).
Author: Dr. Srinivasa Rao Konda
Assistant Professor
GPL, State Key Laboratory of Applied Optics, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics, and Physics (CIOMP), Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 77 Ying Ku Road, Changchun, Jilin, 130033, China.
E-mail: ksrao@ciomp.ac.cn, ksrao.hcu@gmail.com
Article links: (1) https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c01490, (2) https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0054337, (3) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107602
