Author: |
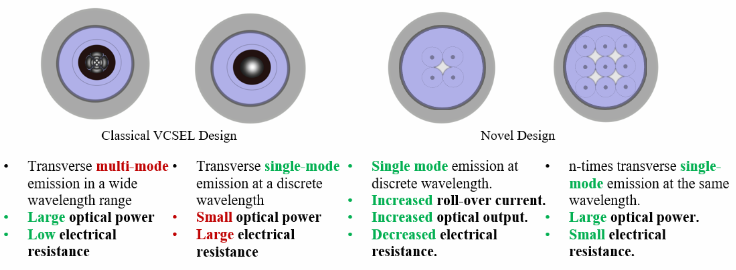
Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VCSEL) are the basis for large data rate optical interconnects in data centers. Presently, VCSELs have replaced edge-emitting lasers for distances below 500 m due to their profound advantages, such as the possibility of testing on a wafer. Our recent development of novel Multi-Aperture and multi-shape VCSELs (patented) at the Bimberg Chinese-Germen Center of Green Photonics at Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), has made a breakthrough in VCSEL processing and brought enormous performance advantages, such as higher temperature roll-over, larger output power, and f3dB, to mention a few.
(Image by Mansoor)
The novel patented design is shown here for the first time. The essence of the novel design is based on the fabrication of variable shape oxide apertures from multiple etched blind holes in any geometric arrangement, which are filled with metal in a second stepto obtain better heat conduction. One mesa may contain one or more emitters that match the 50 μm diameter fiber.
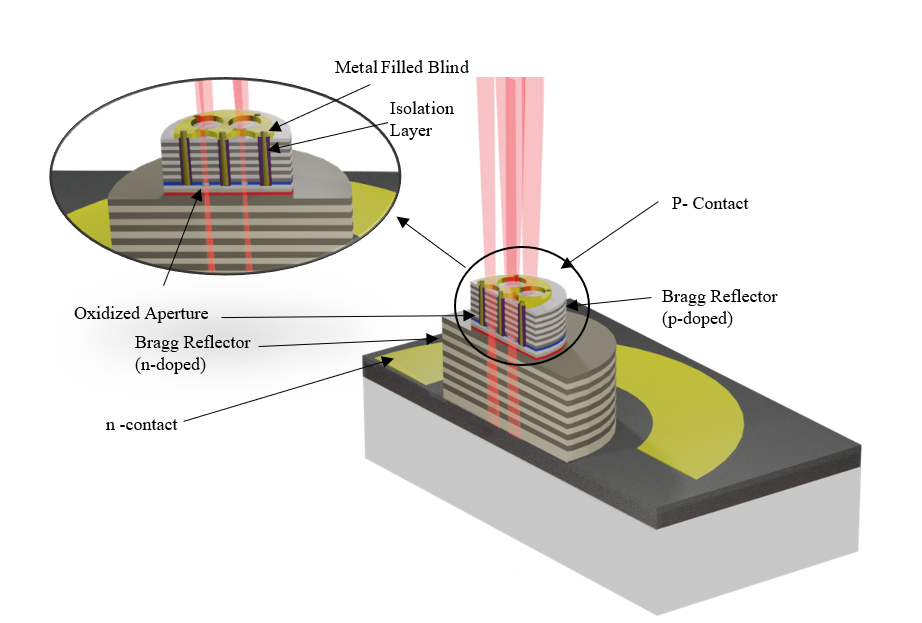
Fig.2 Multi-Aperture VCSELs (Image by Mansoor)
The expected performance advantages of our novel approach include much larger roll-over current for any aperture size, and devices with smaller apertures emit single mode with increasing output power, thus increase communication distance. Furthermore, the apertures with single/multi-mode emission will exhibit smaller series resistance, easing integration with high-speed driver circuits. Multiple emitters can be combined into one device to provide more power for multi-mode fiber. Adjusting the aperture shape can further lead to polarized emission.
Author: Mansoor Ahamed
Bimberg Chinese-German Center for Green Photonics, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, Jilin 130033, China
E-mail: mansoor@ciomp.ac.cn
Article link- Presented at ISLC 2021, Potsdam, Germany (Yet to be published online)
