Author: |
Editor: XIONG Ling | Nov 10, 2021
Researchers led by Prof. XIONG Ling from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) recently developed a pose-varied swing arm profilometer (pvSAP) with increased measurement accuracy for aspheric surfaces. Relevant results were published on Optics Letters.
Swing arm profilometer (SAP) has demonstrated remarkable performance in surface measurement for large aspheric optics since it was proposed in 1990s. Compared to the Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM), SAP can obtain more accurate and efficient measurements with the added advantage of shorter measurement range and crossover sampling.
In a classical SAP mode, the measurement range of the indicator should be larger than the asphericity of the global best-fitting sphere (BFS). As the aperture becomes larger and asphericity becomes higher, the test accuracy decreases as the needed measurement range increases. This aspect is a limitation for improving test accuracy. It would be optimal if an aspheric surface with a higher asphericity could be measured using a probe with a shorter range.
For off-axis aspheric surface, its usual deviated from ideal global BFS. Probe readout for a single scan arc is in a tilted form which can be compensated by rigid motion of the air-table. After removing the tilt of the scan, range of the probe readout is greatly decreased. In other words, by compensating and adjusting the position of the SAP, the sampling of the local BFS basement can be realized, which can shorten the range required for measurement.
Based on the above, a pose-varied SAP (pvSAP) test was proposed. The tilt and piston value of each scan arc was calculated in classical SAP test mode and a new compensated pose of the SAP setup of each scan arcs was determined.
An accurate test comparison for a ?2m off-axis aspheric mirror was conducted (as a standard component), whose asphericity in full aperture was 1.1mm PV and surface error was λ/40 RMS (λ=633nm, CGH test results) measured by the ZYGO Interferometer. Compared to the classical pfSAP test, the measurement range of the required probe was reduced by 50%, and test repeatability was improved by 50% accordingly. Test accuracy was promoted by 32%.
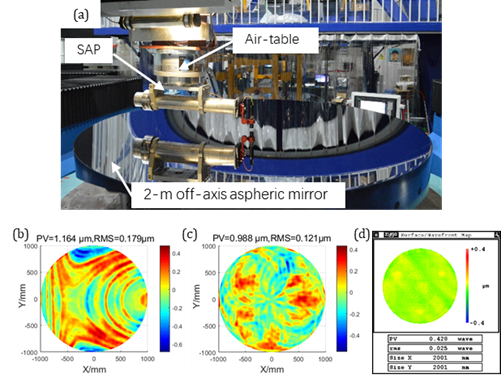
Fig. 1 SAP setup for testing a ?2m standard off-axis aspherical mirror (Image by XIONG).
Author: Prof. XIONG Ling
Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Changchun, Jilin 130033. China
E-mail: xiongling@ciomp.ac.cn
Article links: https://www.osapublishing.org/ol/fulltext.cfm?uri=ol-46-19-4940&id=459964
