Author: |
Editor: ZHAO Zhen | Nov 04, 2021
In a study published in Nanomaterials, Dr. ZHAO Zhen from Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and his collaborators found that single uniform nanowire can be fabricated by femtosecond laser with the help of a groove.
Single Nanowire, a fundamental structure element, is widely employed in modern photonic equipment, because of its fascinating capabilities in manipulating light. Compared with traditional fabrication method of microstructures, laser-induced periodic surface structure (LIPSS) has attracted considerable interests for the advantages of convenience and no need for masks. However, LIPSS usually consists of numerous nanowires of uncontrolled formation number. How to fabricate single nanostructure remains an open question.
The researchers selected the Fe-based metallic glass surface with prefabricated groove as the sample as the groove can effectively focus light energy and guide the formation of energy difference, i.e., the groove occupies higher energy distribution compared to the smooth surface. The atomic force microscope shows the V-shaped groove feature sizes of both the upper opening width and the longitudinal depth of 600 ± 9 nm and 110 ± 9 nm, respectively.
Under the irradiation of two time-delayed femtosecond laser beams with consistent linearly polarization parallel to the groove, the uniform formation of the single nanowire structure with the width of 118 nm can be observed within the groove. This is the first time that using laser-induced methods to realize the fabrication of single nanowire structure. Moreover, the formation number of the nanowire within the groove can be accurately controlled by changing the feature size of the groove.
Moreover, the researchers also demonstrated the formation mechanism of single nanowire, which can be attributed to two physical ultrafast dynamic processes. Under laser irradiation, the magnetic surface wave on sample surface first excite and interfere with the incident femtosecond laser, resulting in a periodic energy filed formation on the sample. Subsequently, due to the higher energy distribution within the groove, with suitable incident laser energy, the LIPSS can be restricted to only within the groove, while the area outside the groove can remain smooth sample surface.
The study solved the presisting problem of the uncontrolled structure formation number in the field of laser induced structure and presented a convenient solution of single nanowire fabrication.
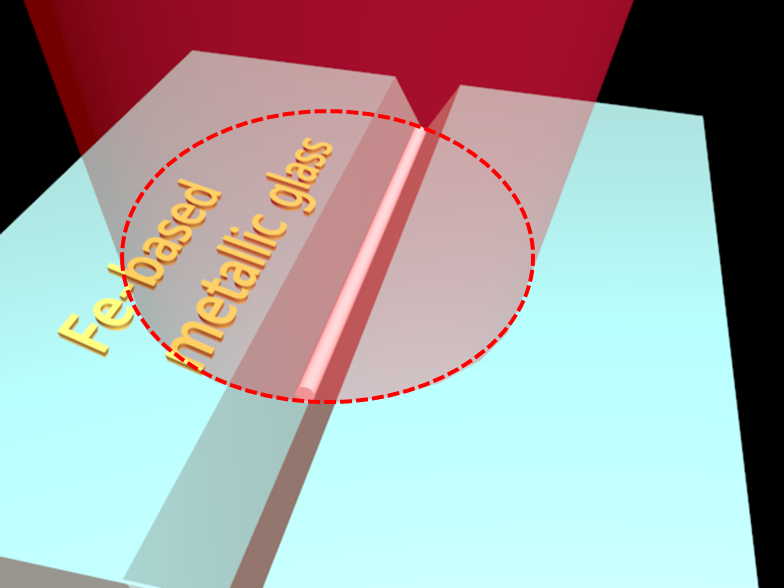
Fig. 1 The schematic image of the single nanowire within the groove fabricated by the femtosecond laser (Image by ZHAO)
Contact:
Author: Dr. ZHAO Zhen
Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, Jilin 130033, China
E-mail: zhaozhen17@mails.ucas.ac.cn
Article links: https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092389
