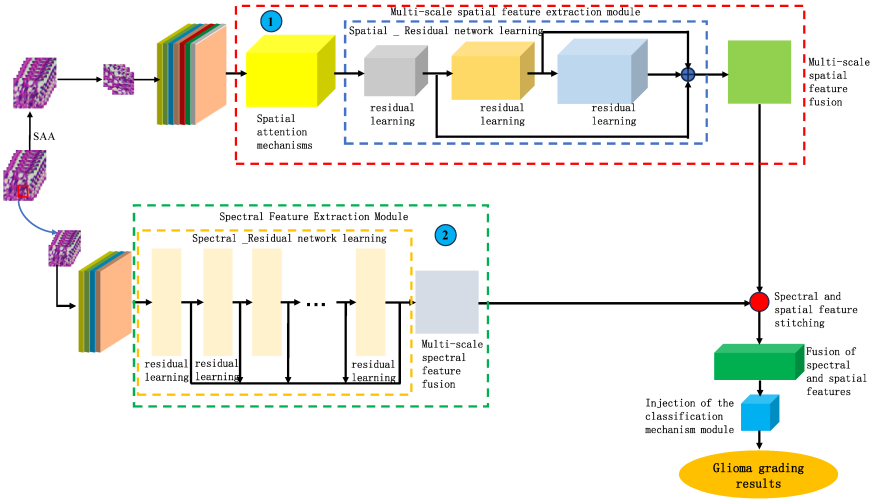
A groundbreaking study by researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has successfully developed an automated method to determine the malignancy grade of glioma pathological sections. Published in the renowned journal Sensors, the research presents a novel hyperspectral imaging system and a feature extraction model, SMLMER-ResNet, that significantly advances the precision and efficiency of glioma grading.
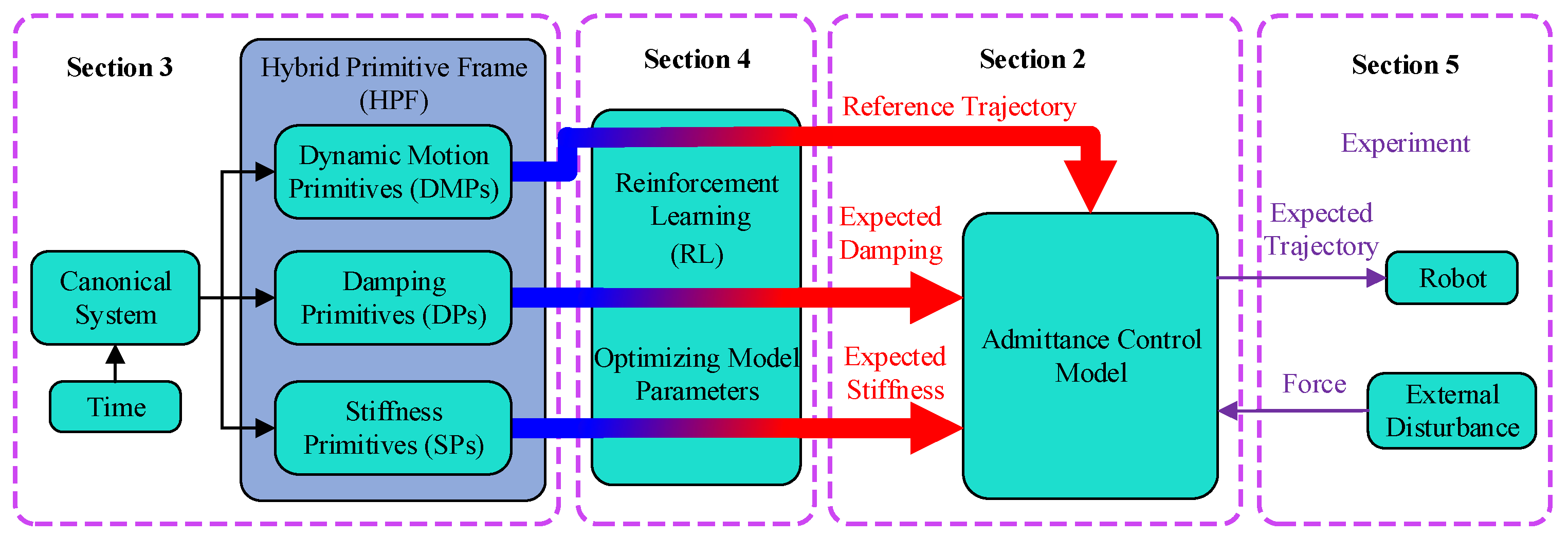
Scientists from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, have developed a groundbreaking robot learning method that endows robots with human-like arm skills. Published in the journal Sensors, the study introduces a hybrid primitive framework that significantly enhances robots' motion flexibility, adaptability, and skill acquisition.
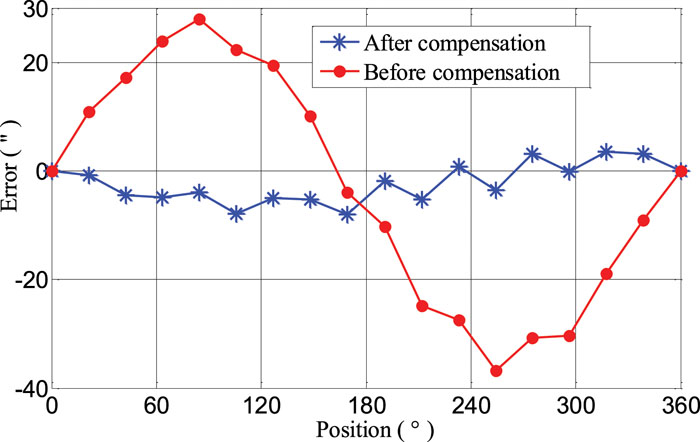
Scientists from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, affiliated with the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have successfully developed a new automatic compensation system that significantly reduces eccentricity errors in optical encoders, a breakthrough that promises to enhance measurement accuracy in industrial applications.This achievement, published in the renowned journal Review of Scientific Instruments.
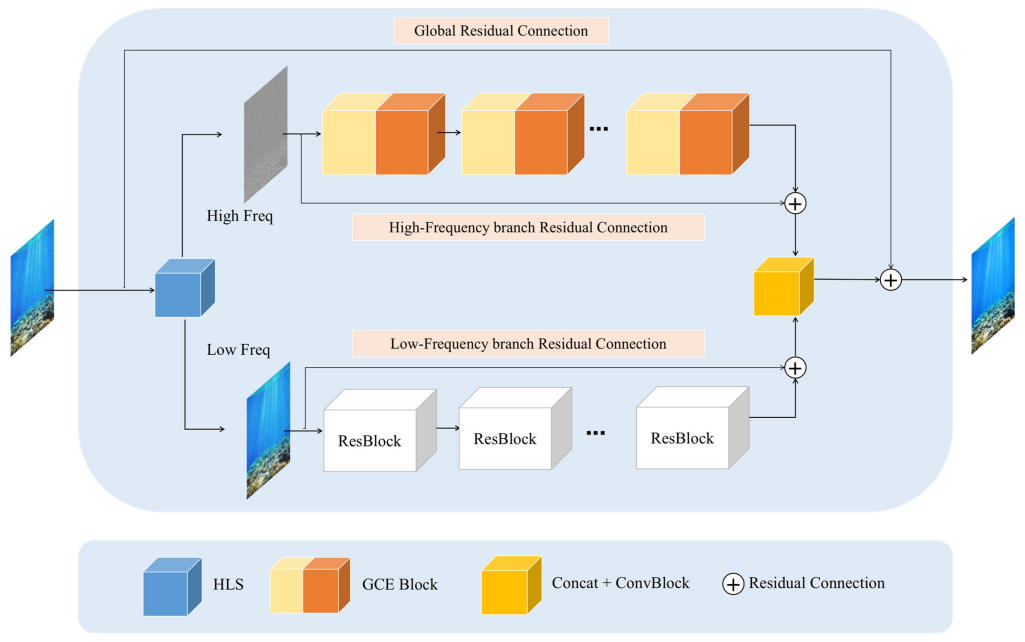
Underwater imaging has gained significant attention in recent years due to its applications in marine exploration, archaeology, and underwater robot operations. However, images captured underwater often suffer from noise, blurring, and color distortion caused by the scattering and absorption of light by water molecules and suspended particles. These issues significantly degrade image quality, hindering effective analysis and operations.
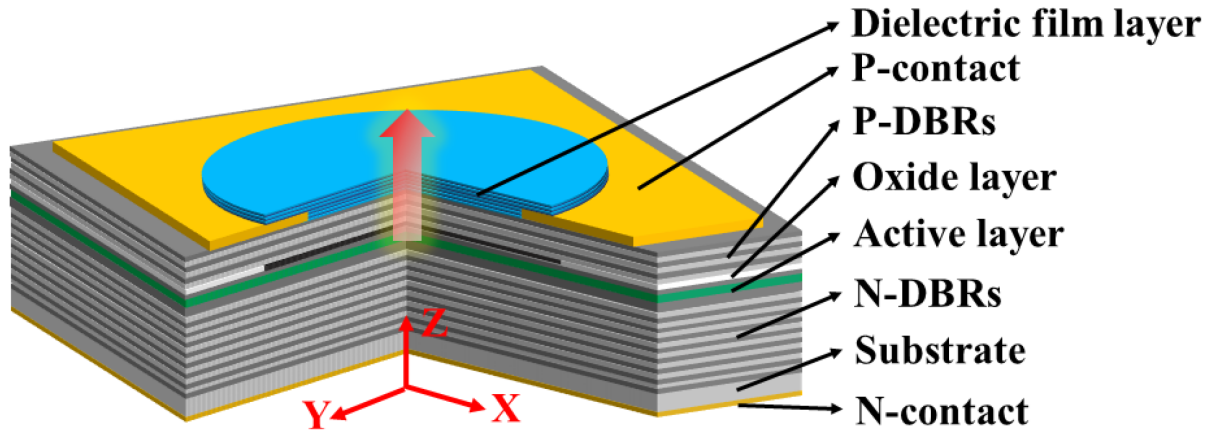
The study addresses the challenges of achieving single-mode output in VCSELs, which are crucial for applications such as optical storage, laser printing, and 3D sensing. Traditional oxide-confined VCSELs often struggle with increased series resistances and low output power when operating in single mode. To overcome these limitations, researchers proposed using metal apertures as an effective mode filtering technique.
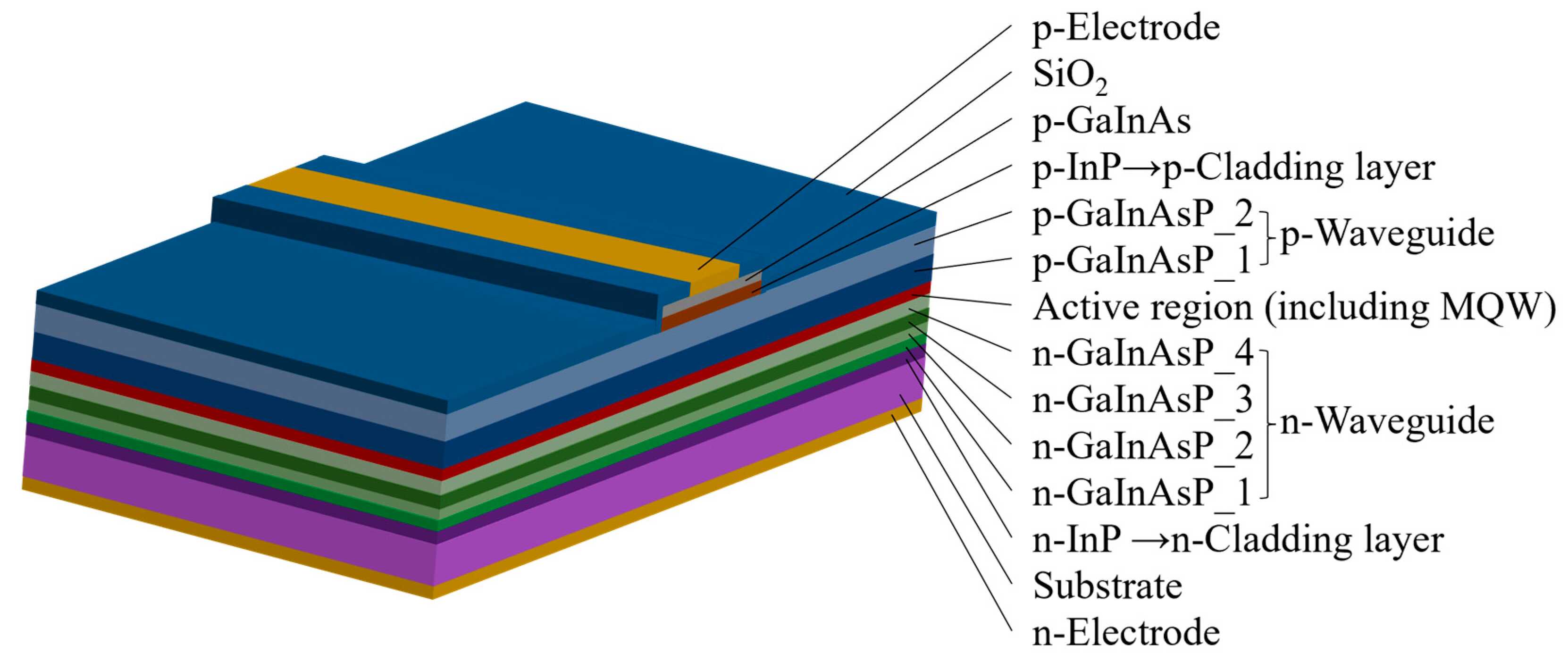
A team of researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics, and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has made significant progress in developing low-polarization, broad-spectrum semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs). In a study published in the journal Nanomaterials, the team presented an innovative SOA design that promises to enhance the performance of optical communication systems, particularly in the context of 6G networks.
