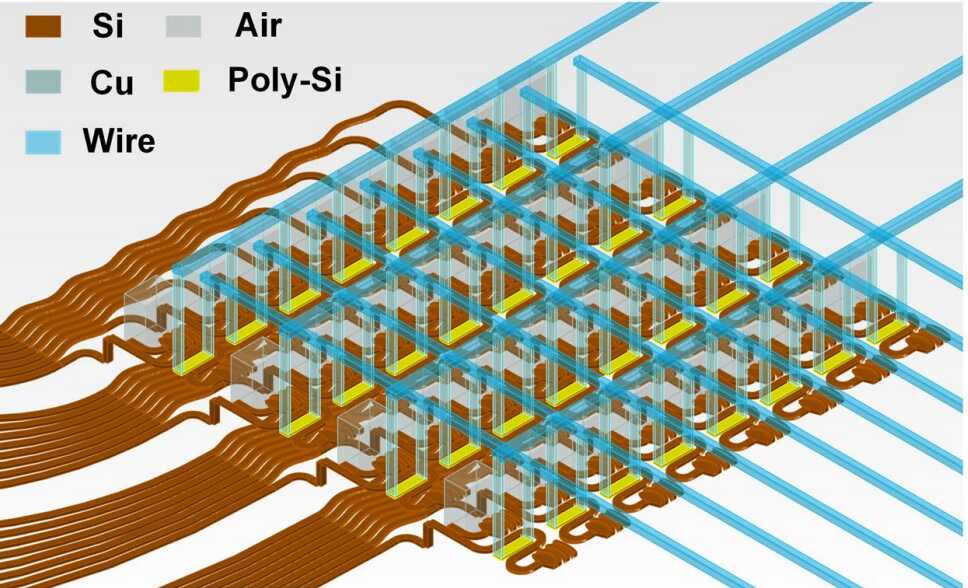
Researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with the Institute of Semiconductors of CAS, developed a double-layer silicon-based optical phased array (OPA) that significantly expands the scanning range of chip-scale LiDAR systems. The study was published in Scientific Reports.
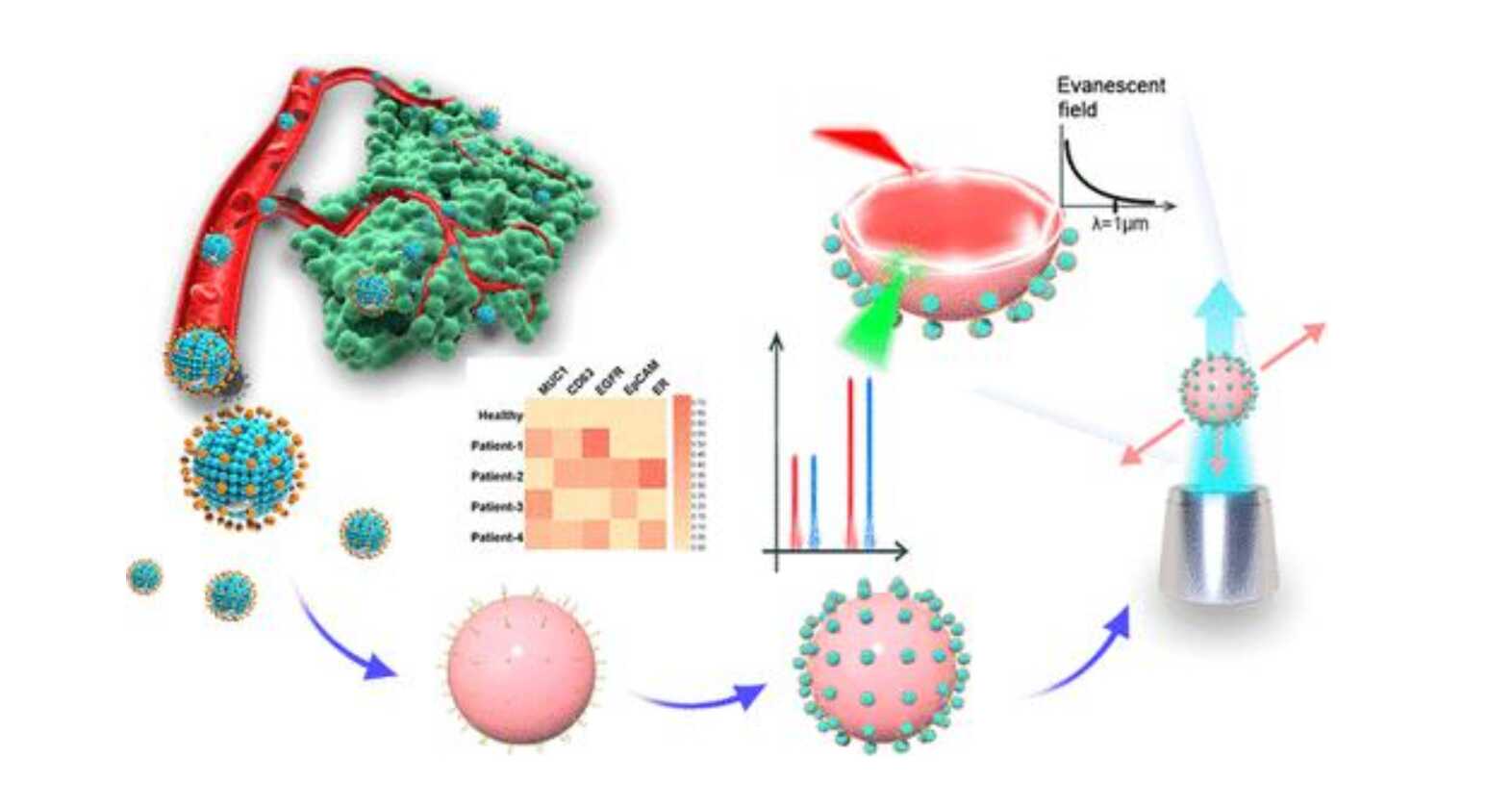
Researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with the National University of Singapore, have engineered a dynamic "laser needle" to solve a century-old problem in optical imaging.
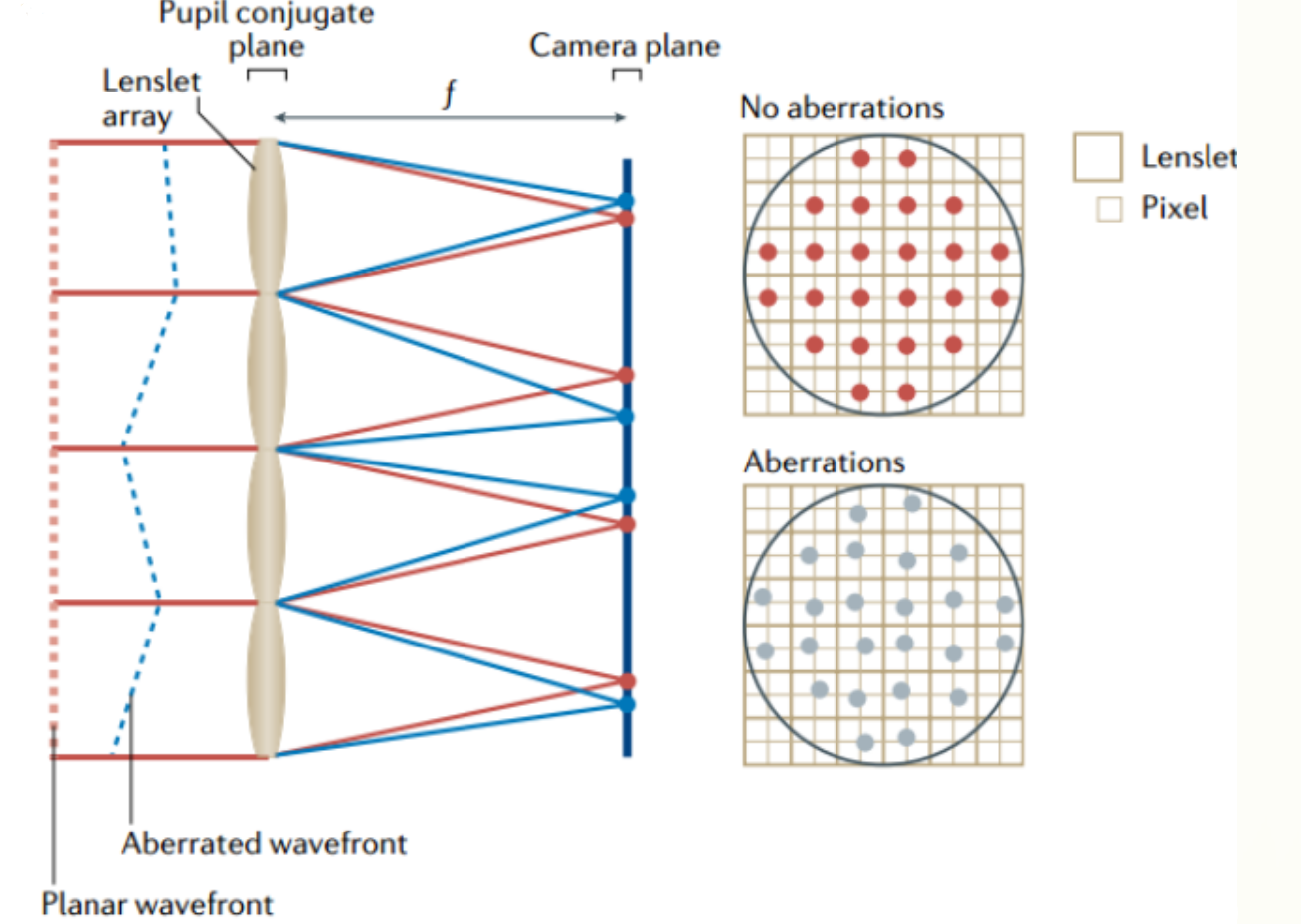
Researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed a novel method using a Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor (SHWFS) combined with "extended sources" to accurately measure the atmospheric coherence length r. This research provides technical support for evaluating atmospheric turbulence in real-time, especially when observing targets that lack point-like light sources or are obscured by high background noise. The results were published in the journal Photonics.
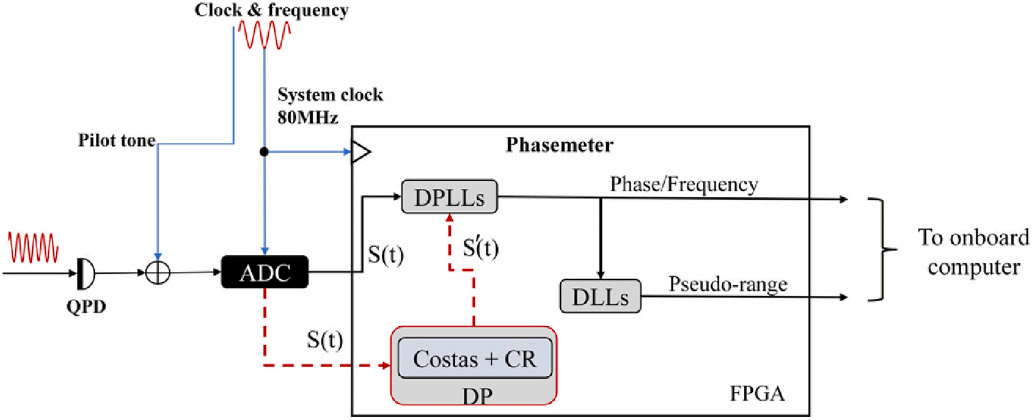
Researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP), Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with collaborators at Changchun University of Science and Technology, reported a hardware-based optimization strategy for intersatellite laser links in Optics Communications. The paper introduced a signal processing architecture combining complex rotation algorithms with error correction coding, effectively solving the interference problem between data transmission and precision ranging in space gravitational wave detection.
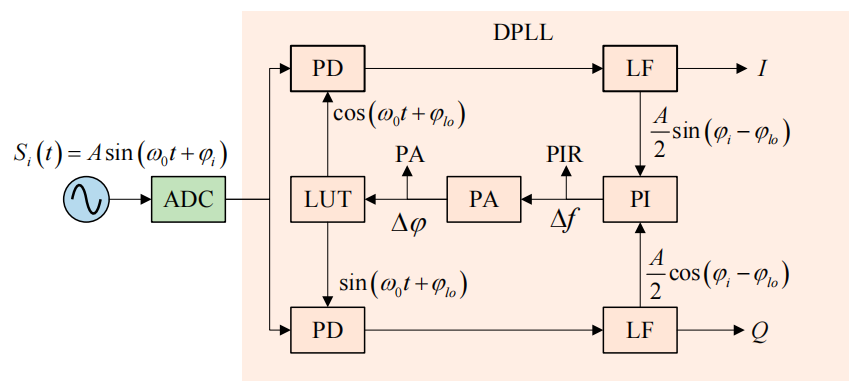
Researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics , Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with collaborators at Changchun University of Science and Technology, reported a key noise evaluation strategy for space-based interferometry in Symmetry-Basel. The paper introduced a comprehensive noise model and a symmetric differential circuit design, significantly reducing the phase measurement error in gravitational wave detection systems.
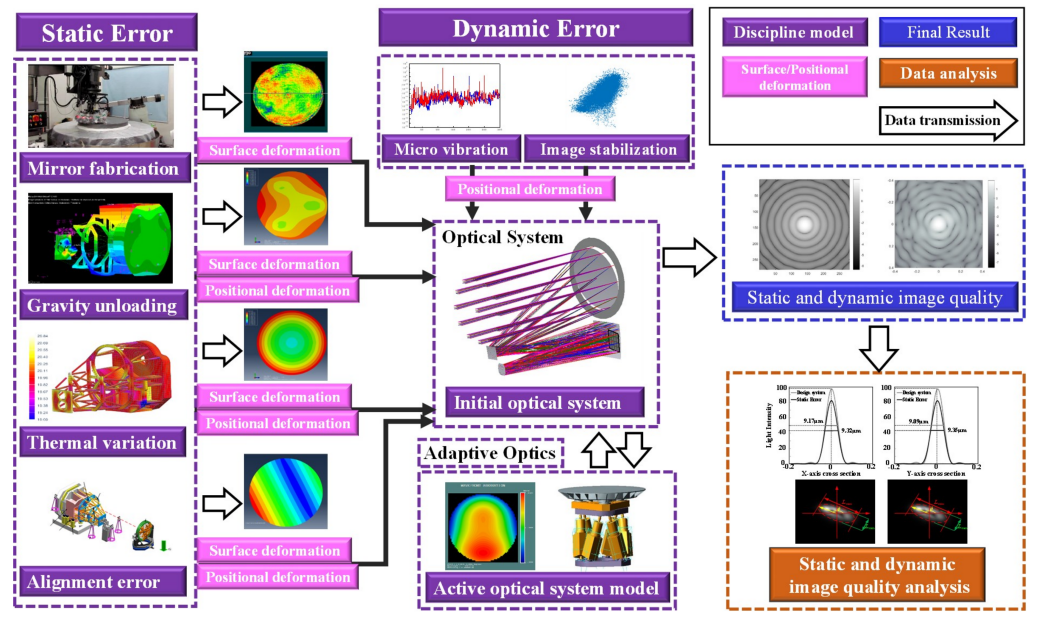
Scientists reported a comprehensive modeling strategy for the China Survey Space Telescope (CSST) in Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics. The paper introduced an end-to-end simulation framework that integrates static and dynamic error models, realizing accurate prediction of the telescope's optical performance under in-orbit conditions.
