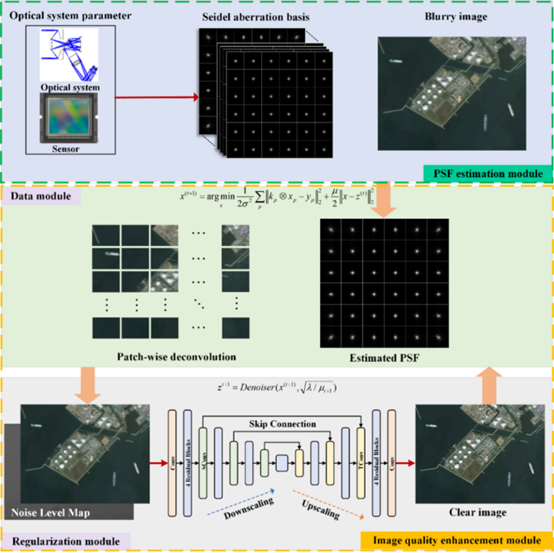
A study published in Scientific Reports by Springer Nature, with researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, introduced a novel method to significantly improve the clarity of images captured by aerial cameras. This approach addresses a persistent challenge in remote sensing: image blur caused by optical aberrations that vary unevenly across the field of view.
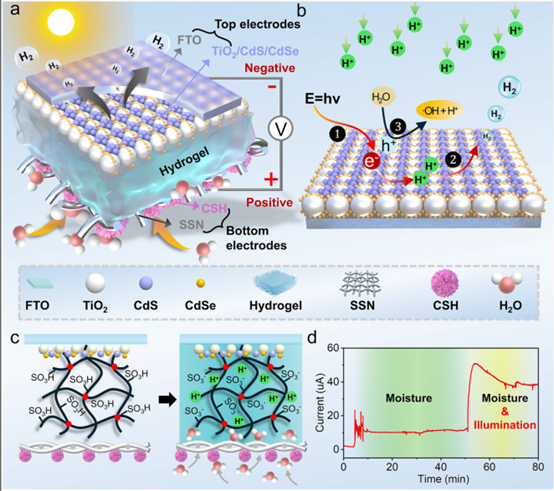
A study published in Advanced Materials by Wiley-VCH GmbH, with researchers from the Changchun University of Technology and the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, demonstrated a new method to significantly improve the performance and longevity of devices that generate electricity from atmospheric moisture. By integrating a light-sensitive component, the team created a device that overcomes a major limitation of conventional moisture electricity generators (MEGs).
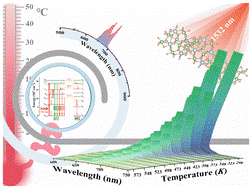
A study published in Dalton Transactions by the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics and the Royal Society of Chemistry, with collaborators from Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications and, reports the creation of a new material that emits high-purity red light when excited by a specific type of near-infrared light. This advancement holds potential for improved temperature sensing deep inside biological tissues and for creating more secure anti-counterfeiting features.
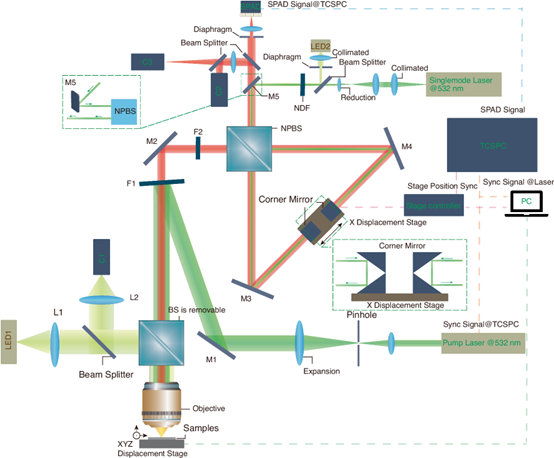
In a study published in Light: Science & Applications by Springer Nature, researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics and Cardiff University developed a novel spectroscopy platform. This system successfully acquired both Raman and fluorescence lifetime images at the same time, overcoming a long-standing challenge in optical spectroscopy.
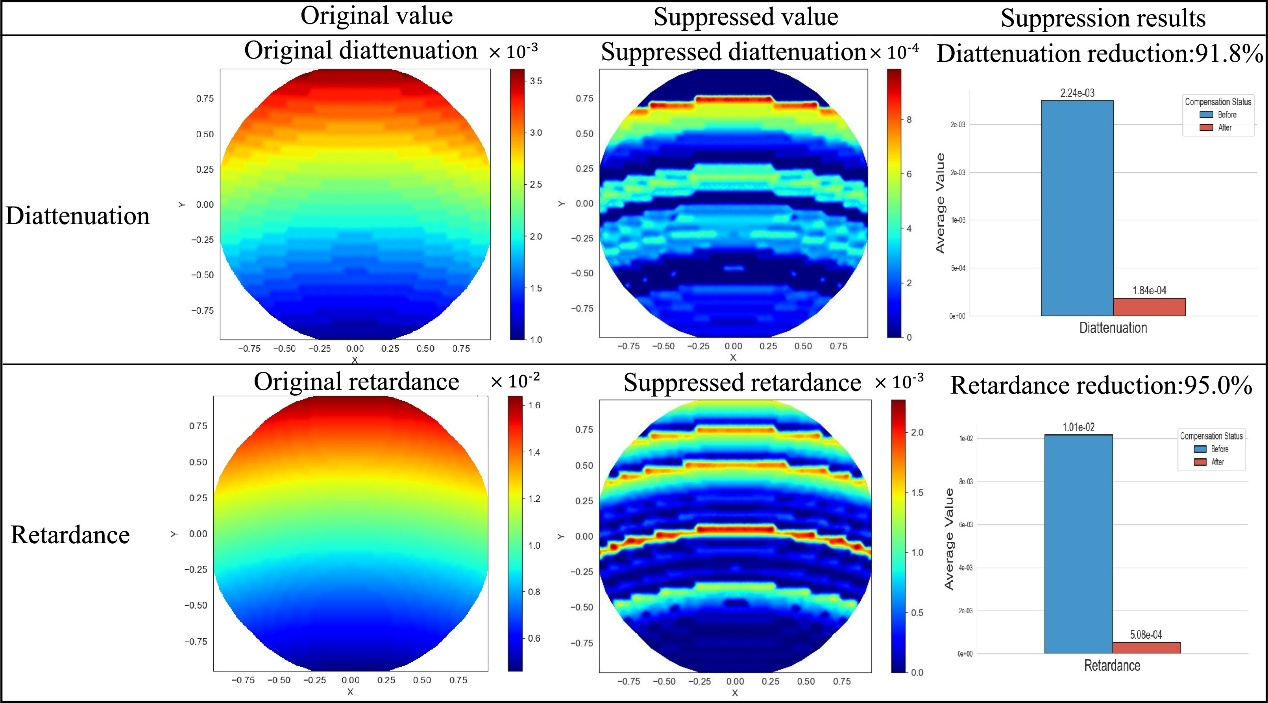
A study published in Optics and Lasers in Engineering by researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, demonstrated a new method to significantly improve the polarization-maintaining performance of optical systems. They achieved this by integrating specially designed metasurfaces, reducing key polarization aberrations by more than 90%.
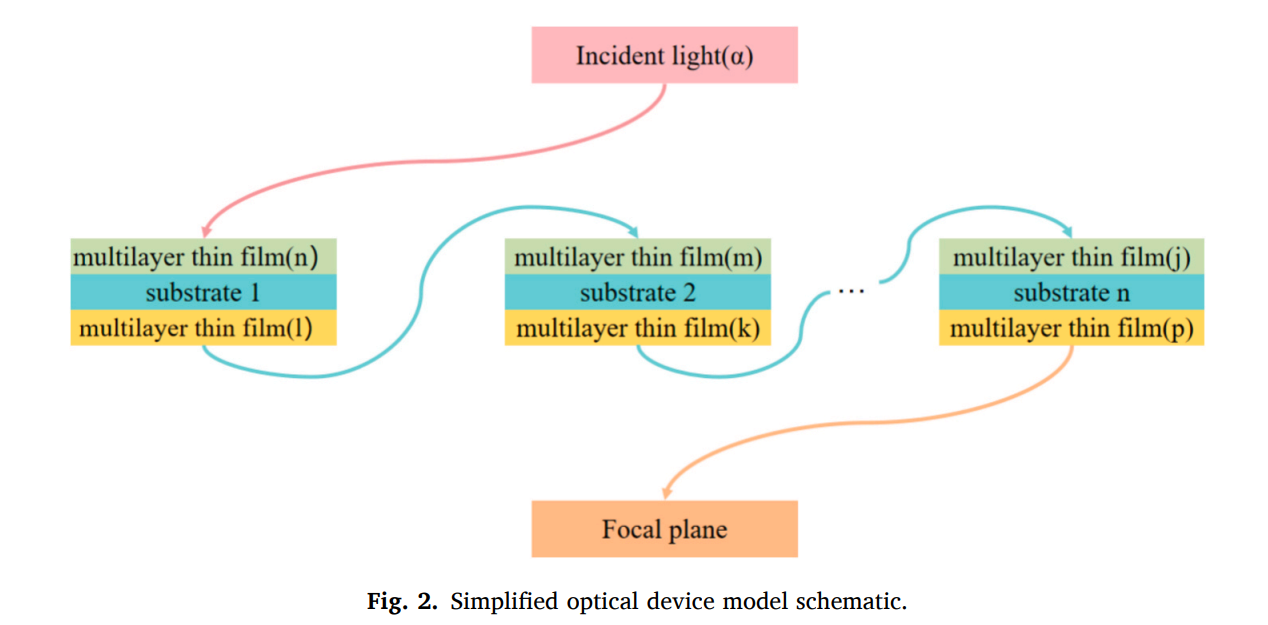
A study published in Optics and Laser Technology by researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, introduced a new theoretical model to analyze and suppress unwanted interference effects in multi-planar interface optical systems. This work addresses a critical challenge in the design of compact, high-performance optical devices used in fields like space exploration and satellite communications.
