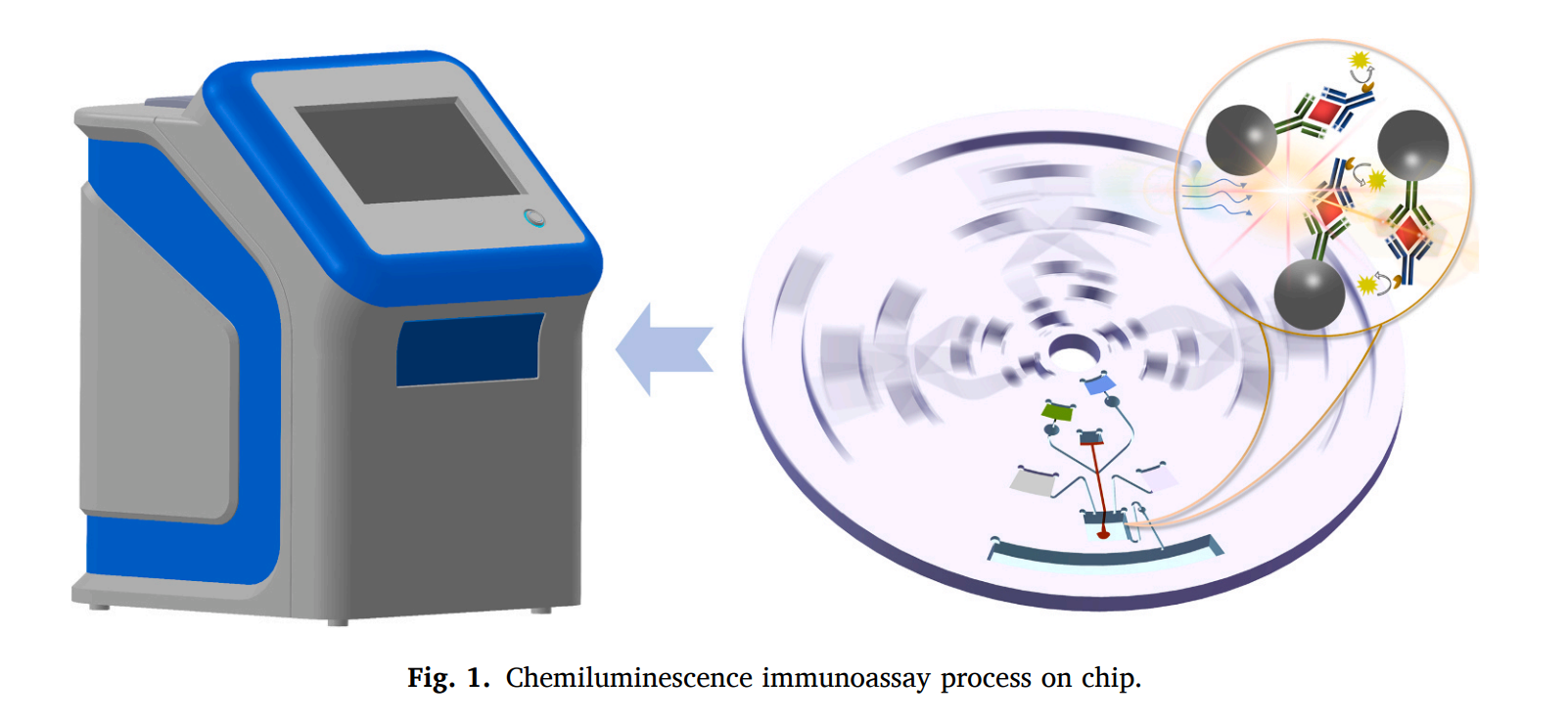
A study published in Sensors and Actuators: B. Chemical by researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, introduced a highly integrated centrifugal microfluidics platform for automated chemiluminescence detection of prostate cancer biomarkers.
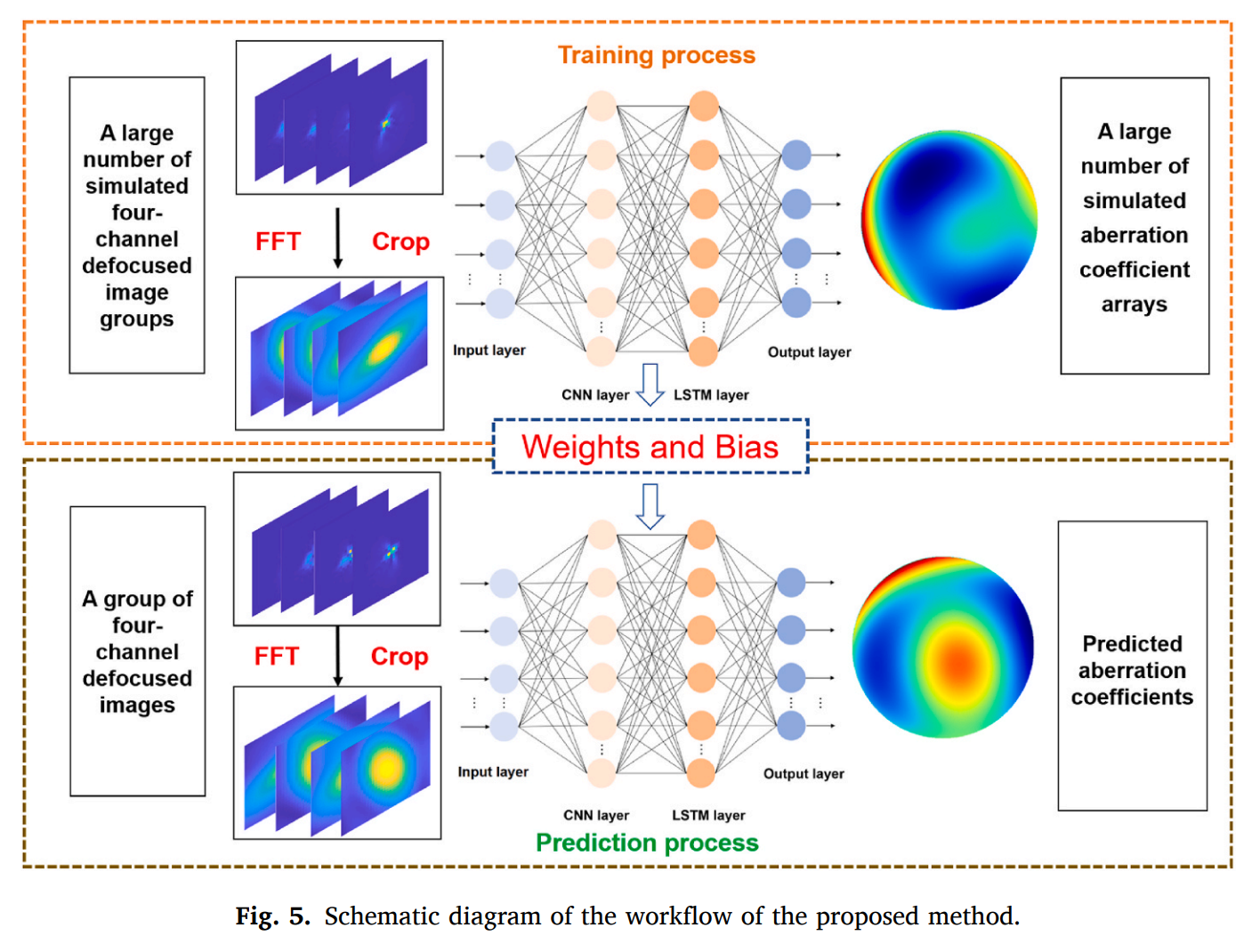
A study published in Optics Communications by researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, introduced a novel deep learning-based approach for accurate wavefront sensing in optical systems that suffer from undersampling.
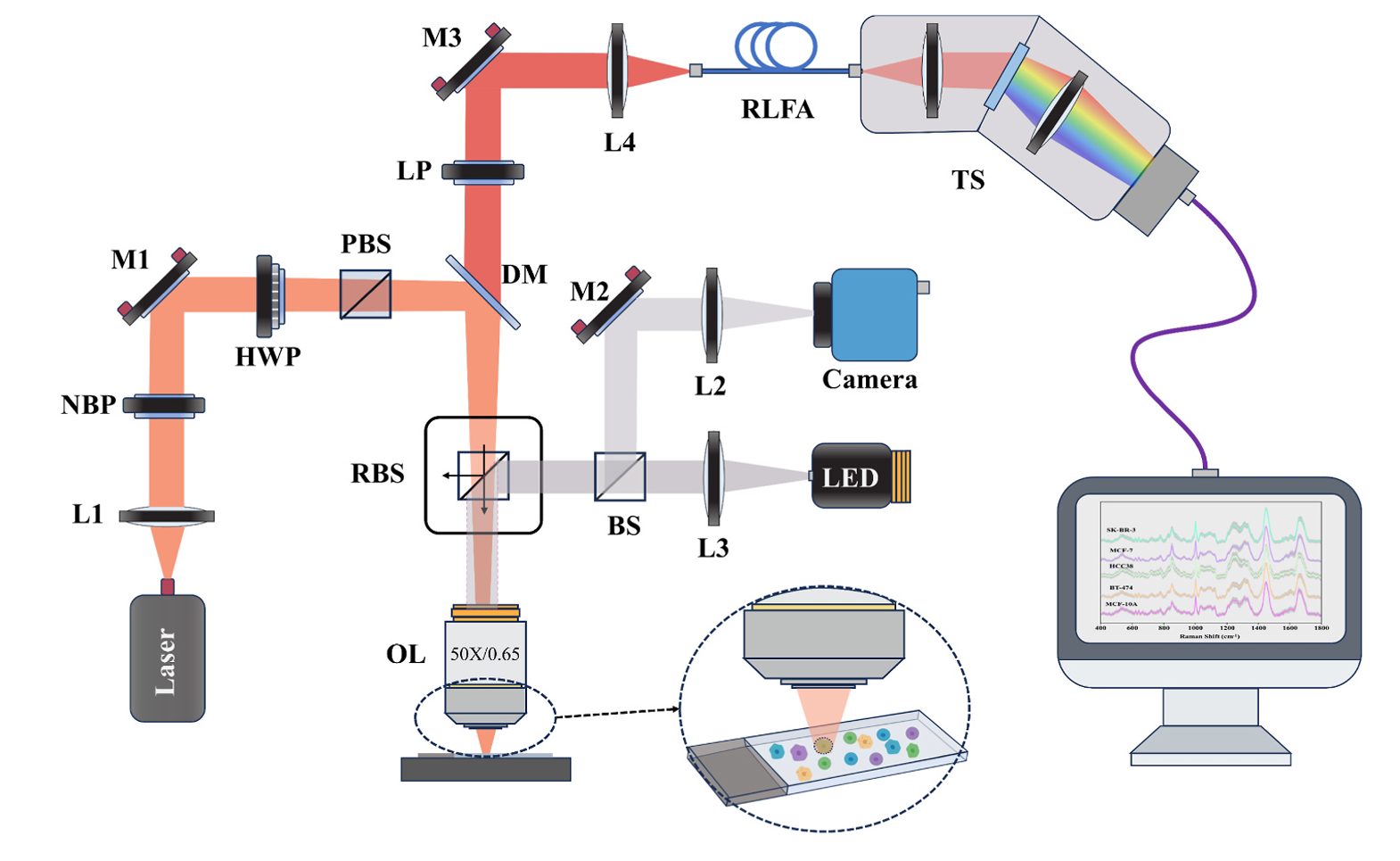
In Talanta, researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences reported an adjustable-spot wide-field Raman spectroscopy system (WFRS-AS) that, when combined with support vector machine (SVM) analysis, more accurately classified breast cancer cells at the single-cell level than conventional Raman setups.
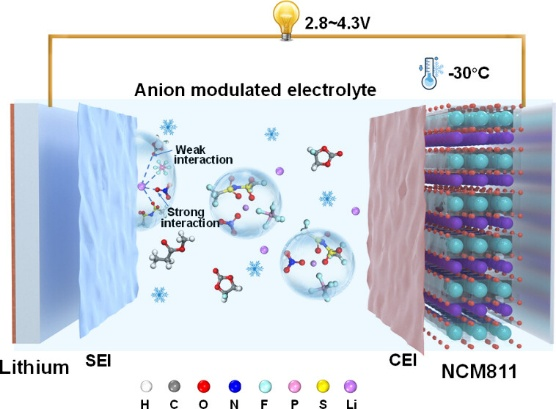
In ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, researchers from the School of Materials Science and Engineering at Shanghai University, the Changchun University of Technology, and the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, reported an electrolyte design that sustains lithium-metal battery performance from −30 °C to room temperature.
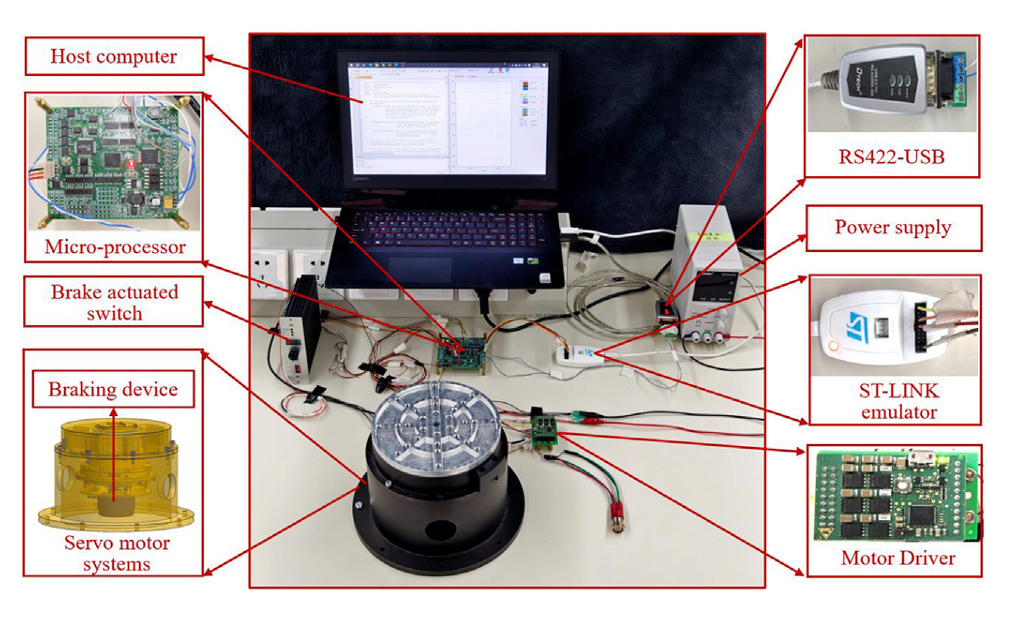
In ISA Transactions, researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, report a compound anti-disturbance method for servomotor position control. The study integrates a novel adaptive sliding-mode disturbance observer (NASMDO) with an adaptive non-singular terminal sliding-mode controller (ANTSMC) to keep tracking accuracy high when disturbances change rapidly.
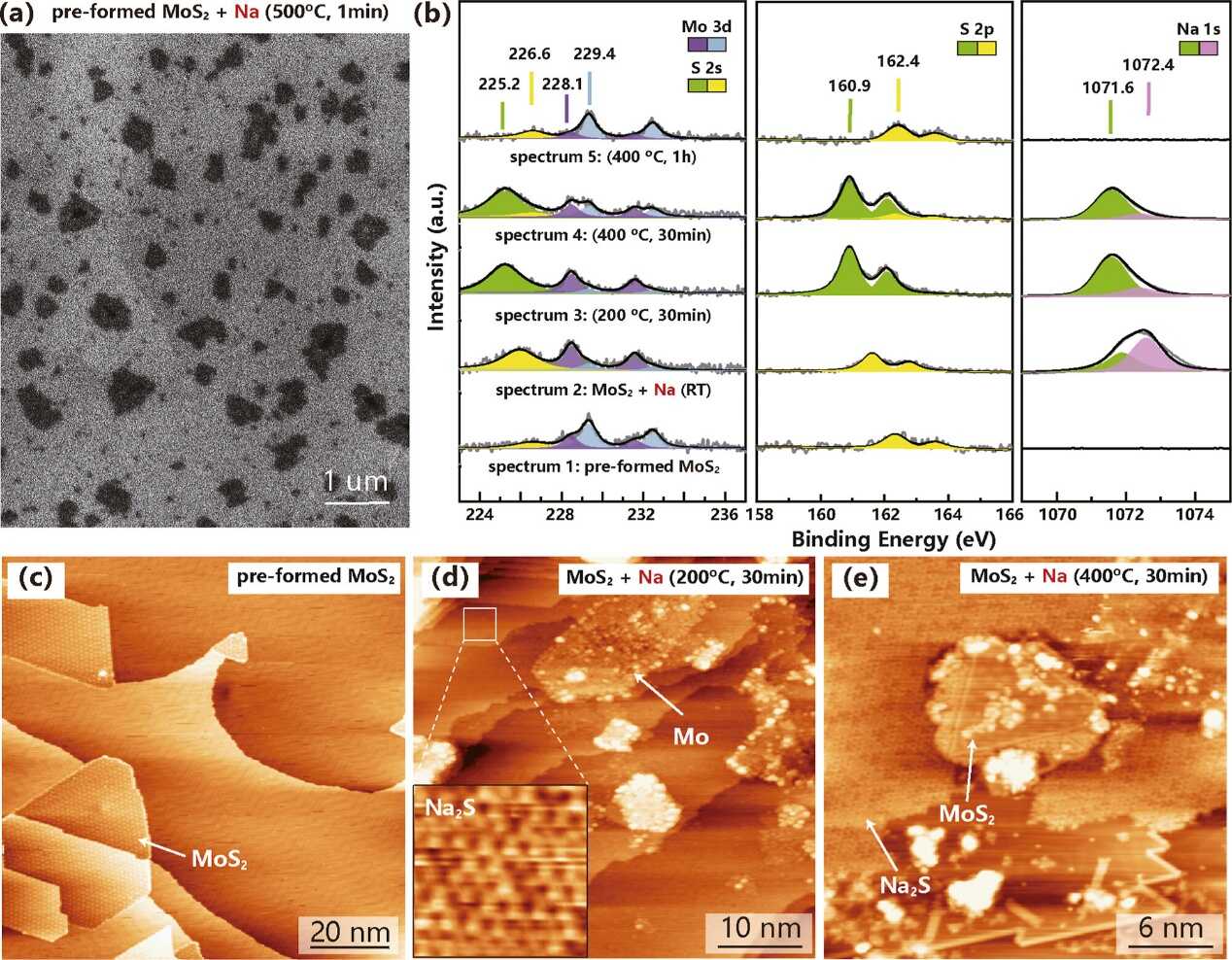
Inorganic Chemistry has published a study from researchers at the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP), Chinese Academy of Sciences, reporting “Na‑assisted molecular beam epitaxy (Na‑MBE)” of monolayer MoS2 on Au(111). The team achieved single‑crystalline domains exceeding one micrometer—an order‑of‑magnitude larger than those grown by standard MBE on the same substrate—while preserving the atomic‑level control that makes MBE attractive for precisely doped two‑dimensional (2D) semiconductors.
