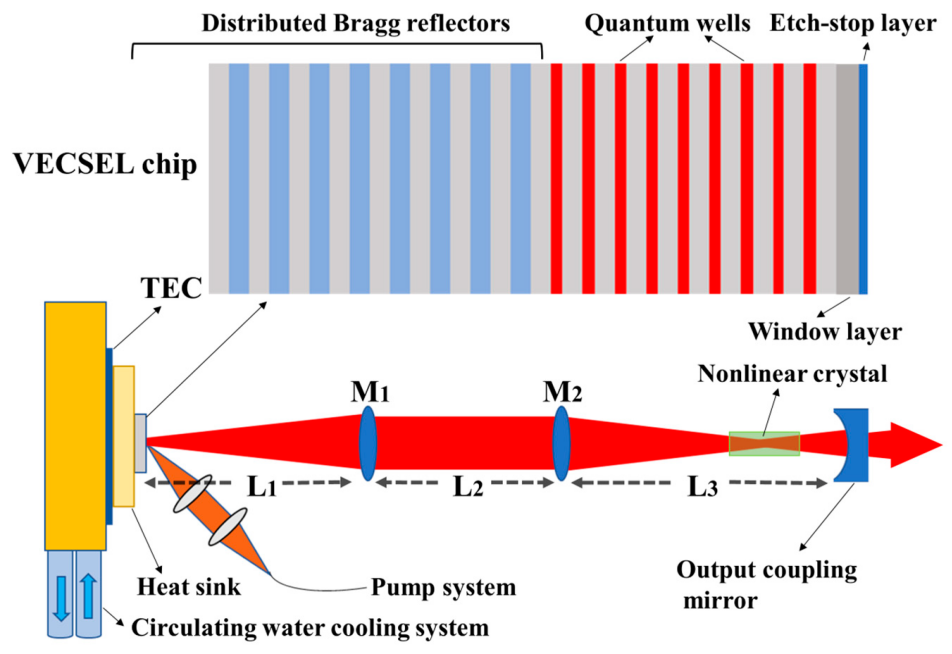
A groundbreaking study conducted by Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has revolutionized blue laser technology through the introduction of intracavity beam-controlled Vertical External Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers (VECSELs). This innovation significantly boosts blue laser efficiency, with profound implications for various industries.
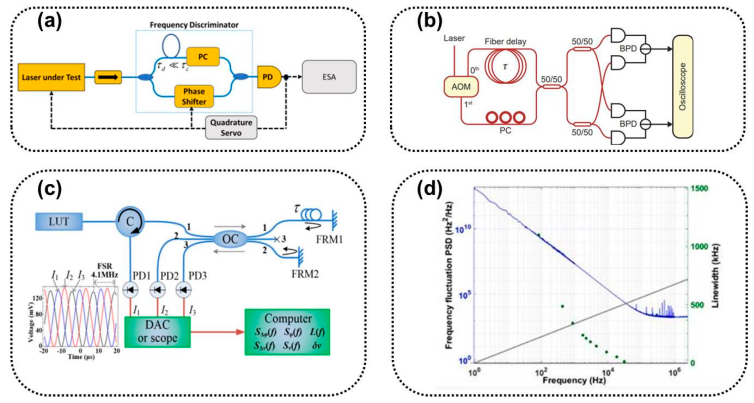
A team of researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences has successfully improved the linewidth measurement accuracy of narrow linewidth lasers, which will be used in satellite laser communications, precision measurements, and ultra-high-speed optical networks. Their study, recently published in Sensors, outlines the principles, methods, and systems used to accurately characterize these high-performance lasers.
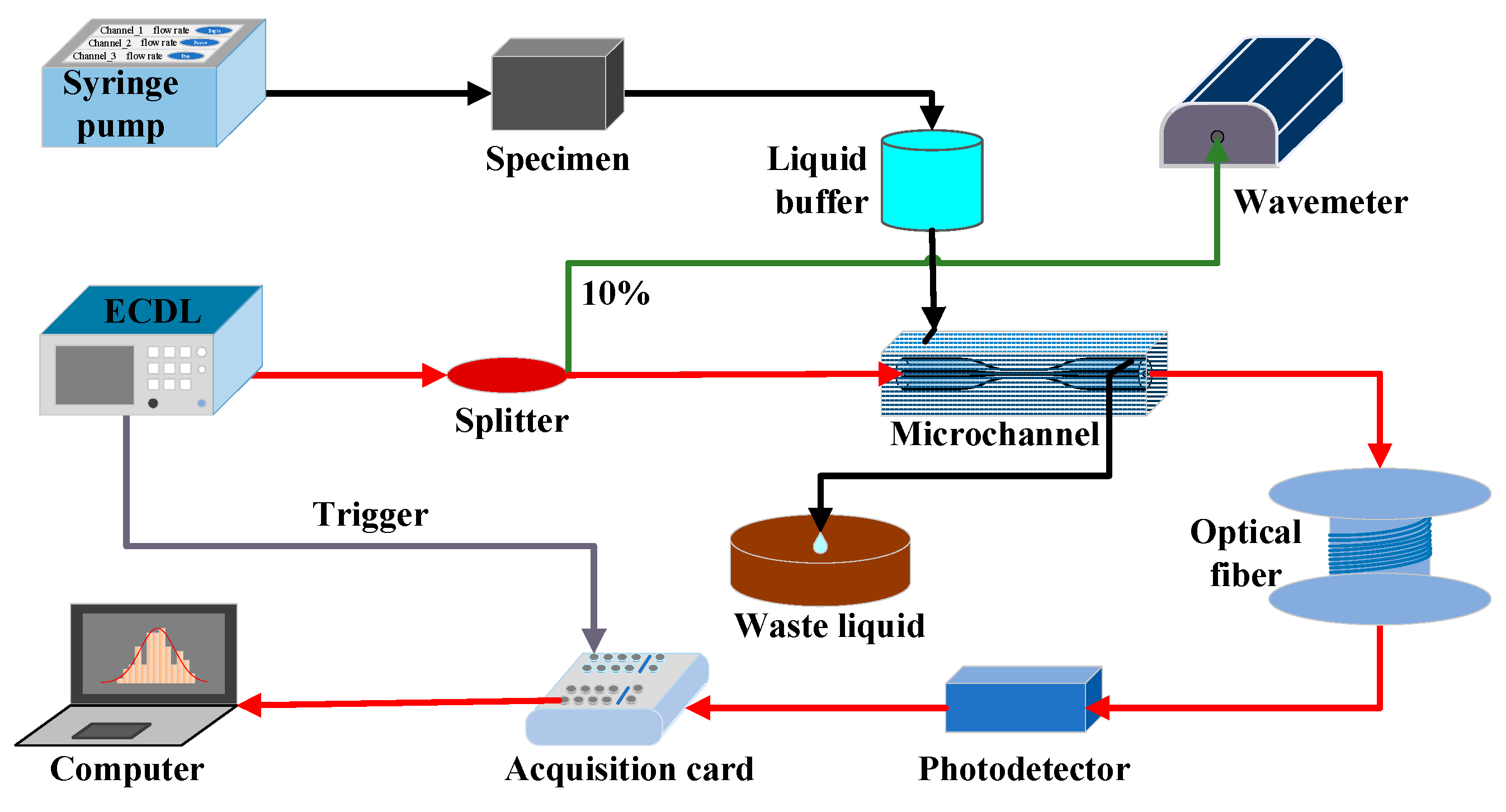
A groundbreaking study led by researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences has introduced a novel technique for directly measuring dissolved gases in aquatic environments using a tapered single-mode silica fiber. This method, published in the journal Sensors, offers a faster and more efficient alternative to traditional membrane-based laser absorption techniques.
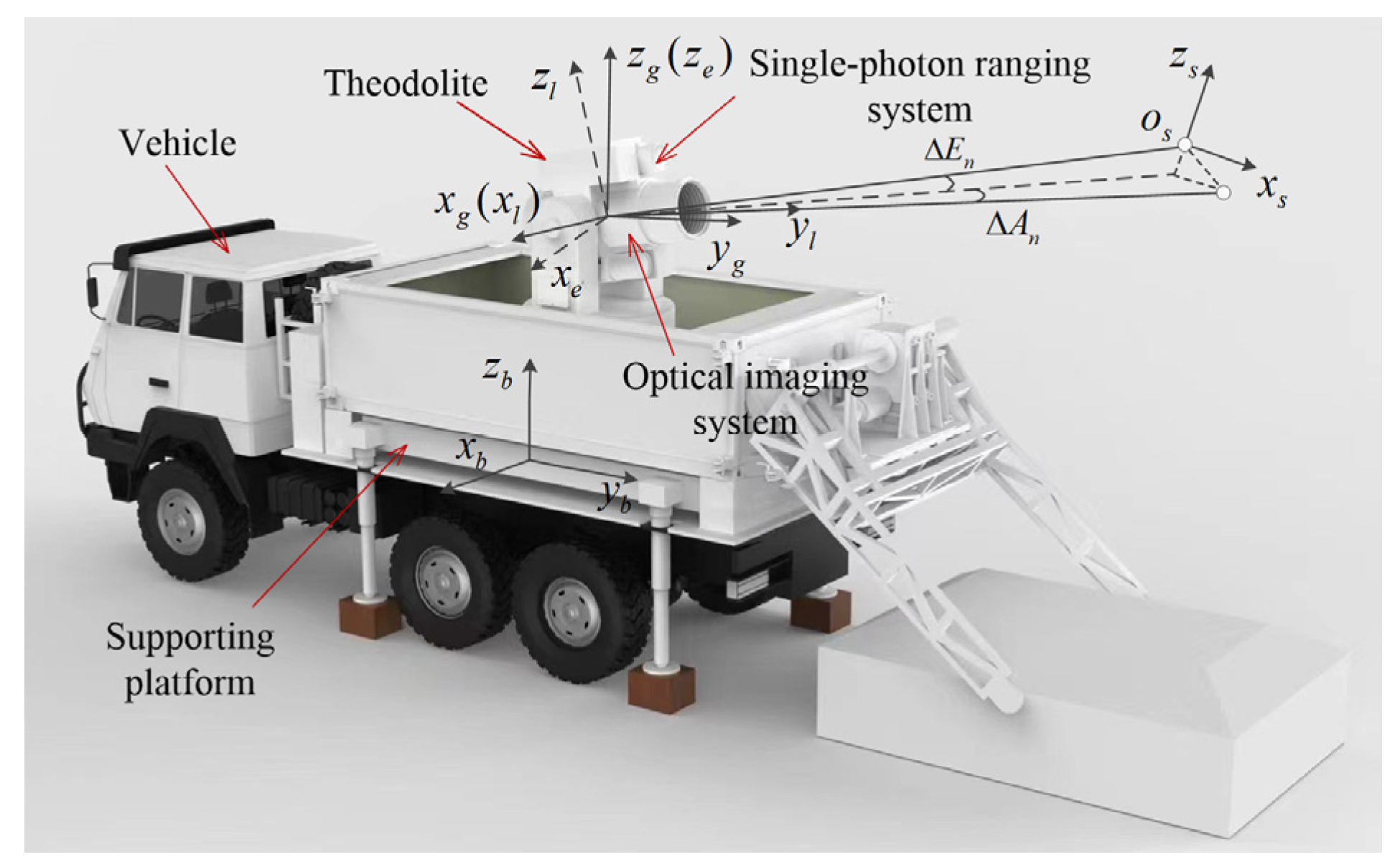
Scientists from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, affiliated with the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have successfully developed a novel and cost-effective pointing error correction method for vehicle-mounted single-photon ranging theodolites (VSRTs). This achievement, published in the renowned journal Sensors, offers a significant improvement in the precision of VSRTs while minimizing financial outlays.
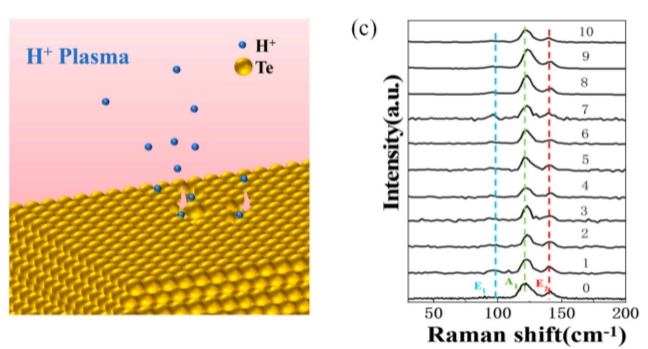
A breakthrough study by researchers from Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, and Chongqing University has revealed a novel method to manipulate the electronic properties of tellurium crystals using plasma irradiation.
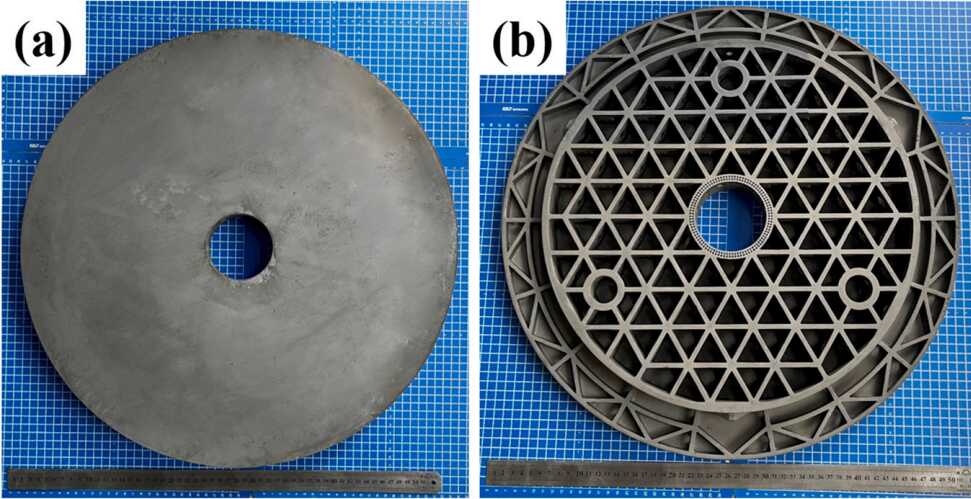
Scientists from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics have achieved a significant breakthrough in the development of high-performance silicon carbide (SiC) mirrors. Utilizing the vat photopolymerization technique (VPP), they have successfully reduced the residual silicon and carbon content in SiC composites, enhancing their mechanical properties and paving the way for more efficient and reliable optical systems.
