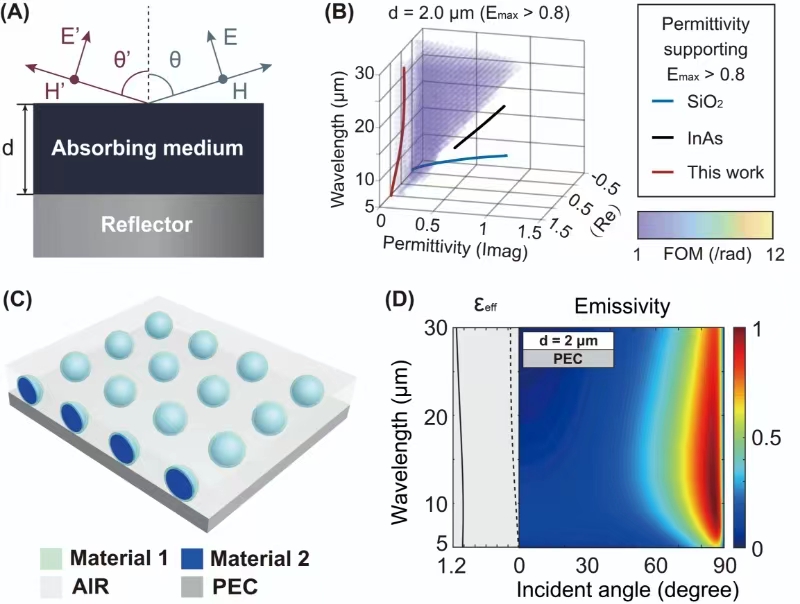
Researchers from Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics led by Prof. LI Wei have established a universal approach to realizing ultra-broadband directional thermal emitters based on effective medium theory (EMT).
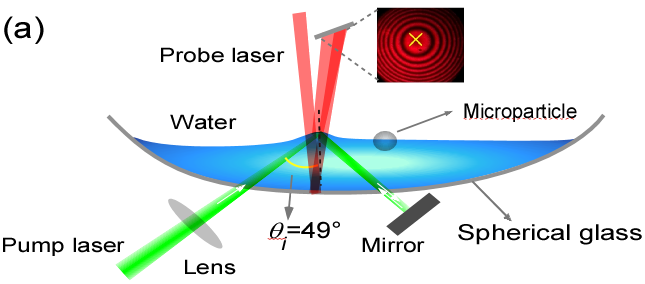
Scientists from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), along with their collaborators, have recently discovered micromanipulation with tunable opto-fluidic curvature. The study was published in Laser Photonics & Reviews.
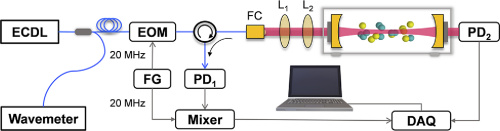
Recently, in a study published in Optics Letters, a research group led by Prof. WANG Qiang from Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a new convenient approach to directly calibrate the cavity-mirror reflectivity for cavity-enhanced gas sensing using Pound-Drever-Hall (PDH) signals.
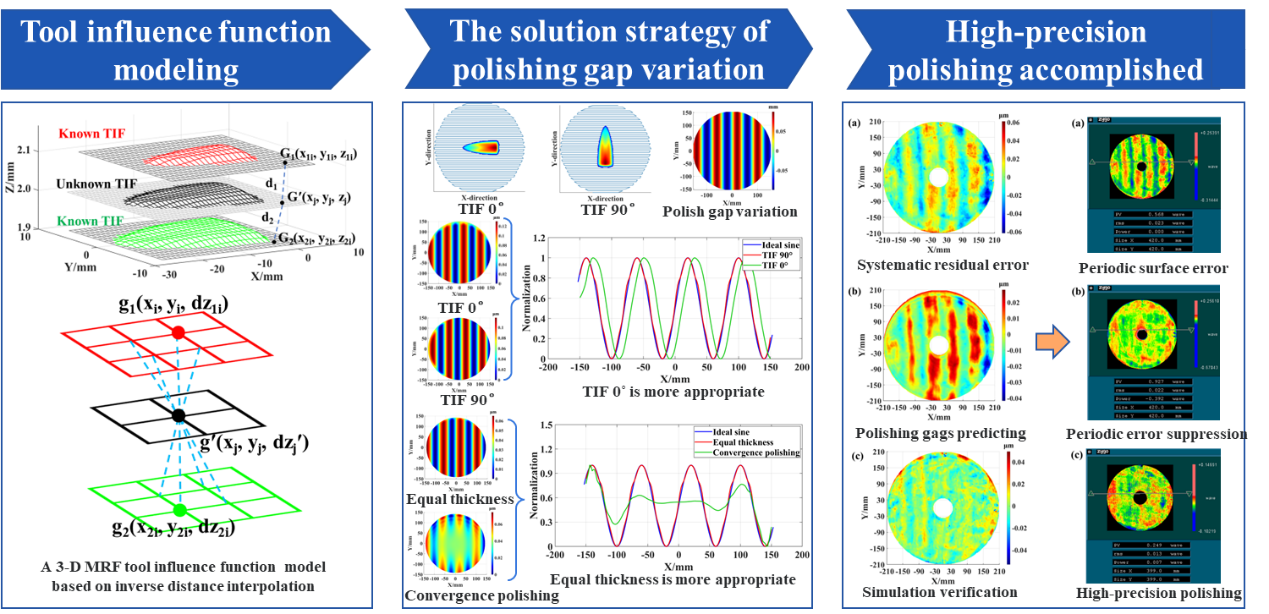
In a study published in Optics Express, a research group led by Prof. ZHANG Xuejun from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a high-precision robot-MRF polishing strategy based on variable tool influence functions (TIFs) and surface shape errors of polished optics to achieve high-precision polishing without compensating for trajectory errors.
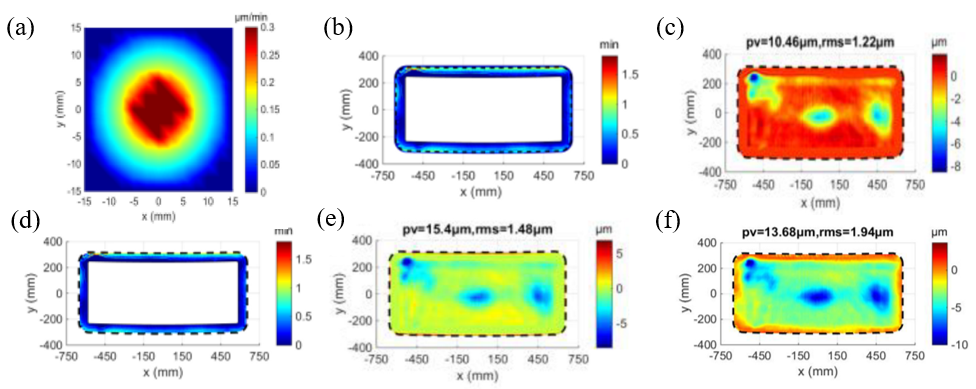
In a study published in Results in Physics, a research group led by Prof. ZHANG Xuejun from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed an optimized strategy ensuring relatively complete convolution of the dwell-time algorithm to control the mid-spatial-frequency surface error and simultaneously ensure high optical manufacturing efficiency.
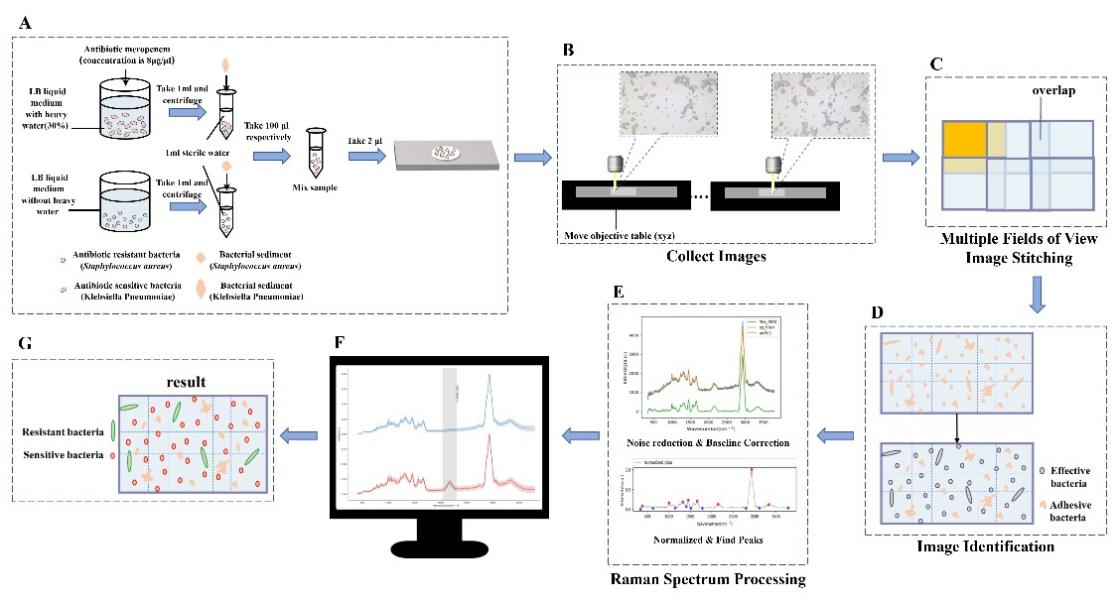
In a study published in Frontiers Bioscience-Landmark, a research group led by Prof. LI Bei from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fin Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Wenzhou Medical University, proposed a detection and analysis method of bacterial Raman spectroscopy based on image stitching and automatic identification algorithm can be used for rapid, accurate and fully automated of analysis of the Raman spectrum of all bacteria at high magnification with multiple fields of view.
