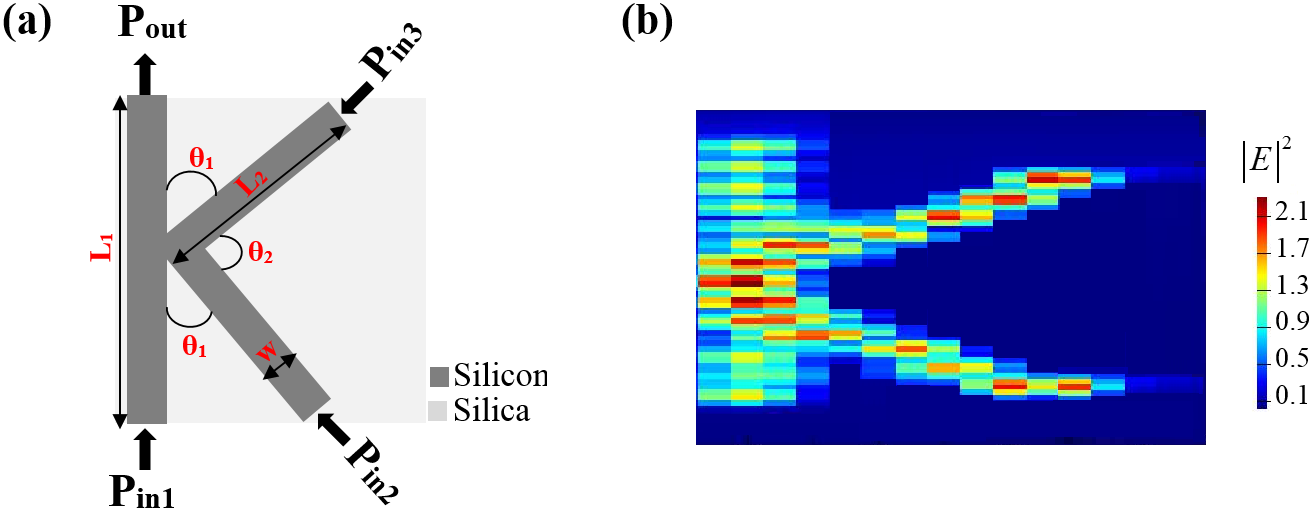
Due to the significant infrared transparency of silicon and refractive index difference between silicon and silica, silicon-on-silica optical waveguides have unique optical features.
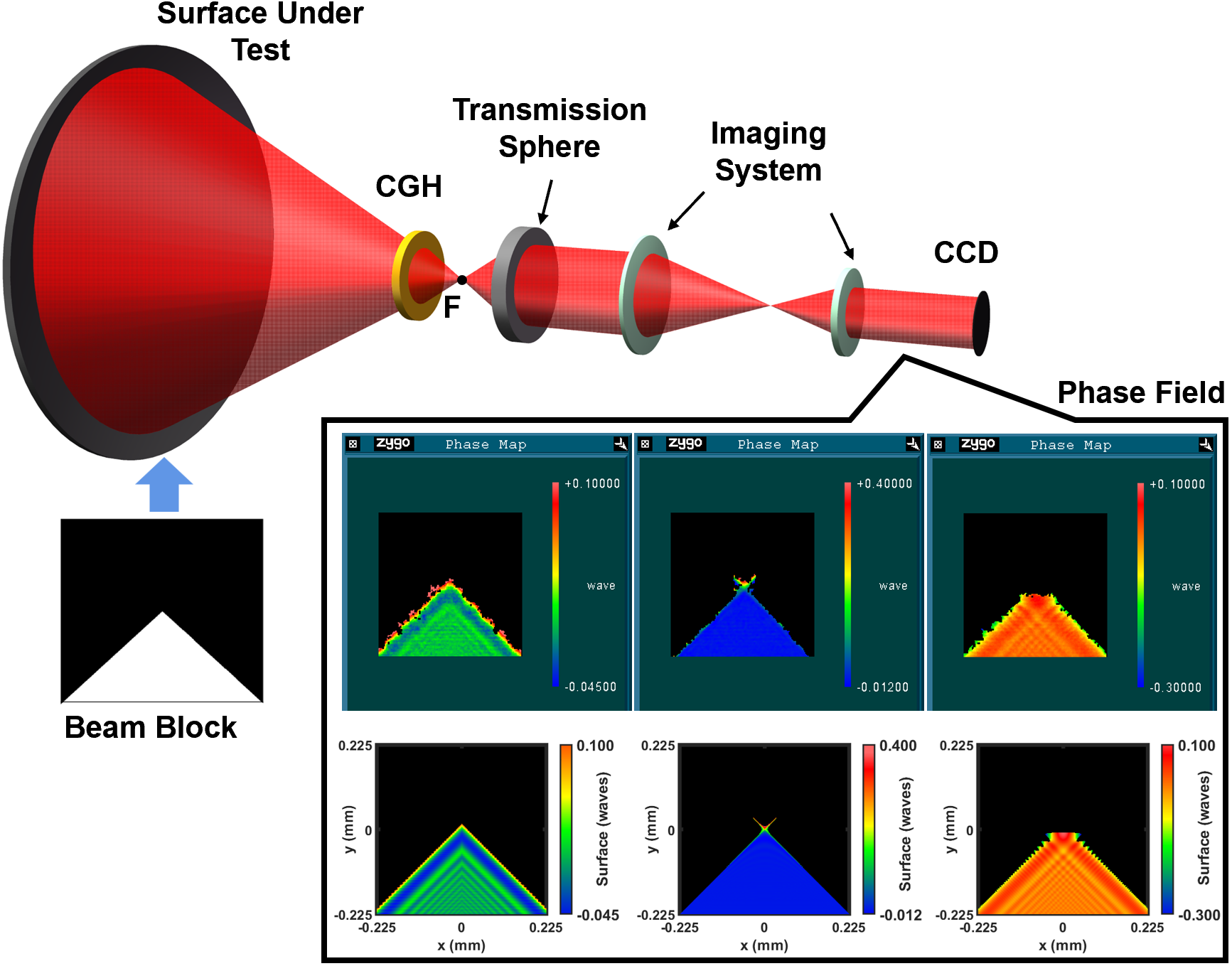
In a study published in Optics Express, a research group led by ZHANG Xuejun from Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a new strategy of improving the instrumental transfer function (ITF) of the CGH interferometric null test.
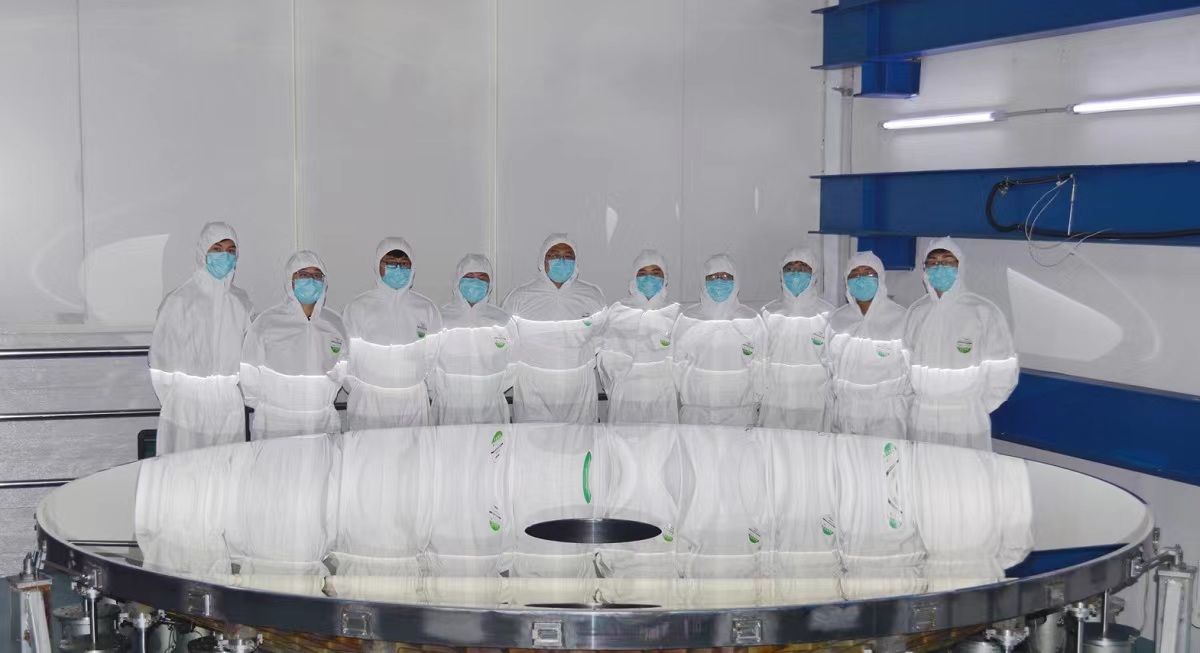

After nearly 20 years of hard work and a series of technical breakthroughs, scientists led by ZHANG Xuejun from Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics (CIOMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have successfully created the world’s largest SiC aspheric mirror, which boasts an impressive diameter of 4 meters.
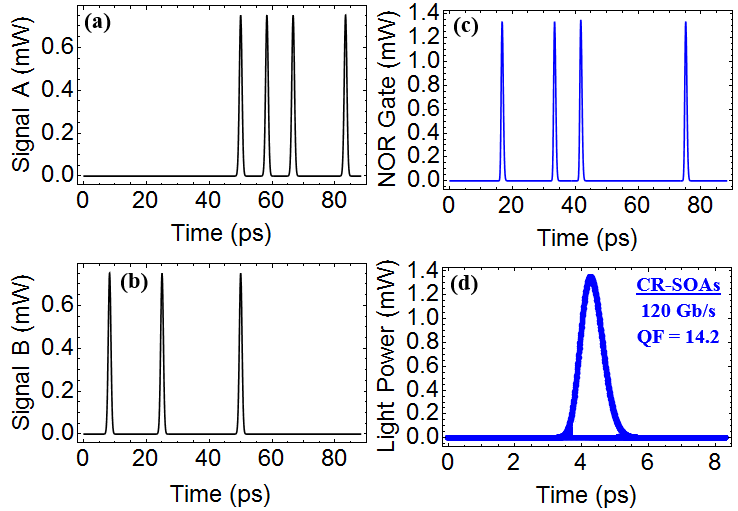
The NOT-NOR (NOR) logic gate is a general-purpose gate that is employed to create any logic operation, build combinational logic circuits, manage packet contention, and monitor bit error rate.
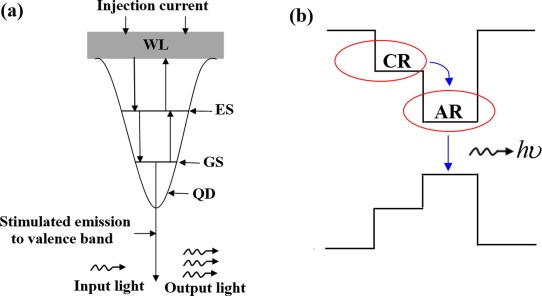
Due to their significance in several applications, including optical networks, optical random memory, and photonic encryption/decryption, optical latches have garnered academic attention.
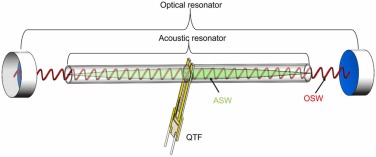
Gas sensors based on photoacoustic spectroscopy (PAS) have advantages of tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS), such as high sensitivity, high selectivity, and wide dynamic range. The sensor performance required is increasingly higher in practical applications.
