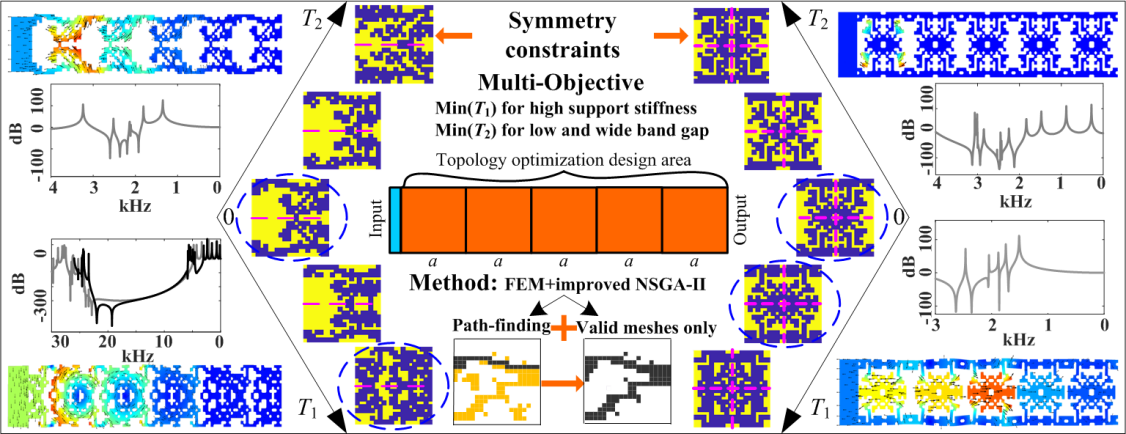
In various engineering fields related to mechanical design, the use of important equipment mostly has the requirements of both lightweight design of support structure and harmful vibration control. But it is often difficult to be considered together.
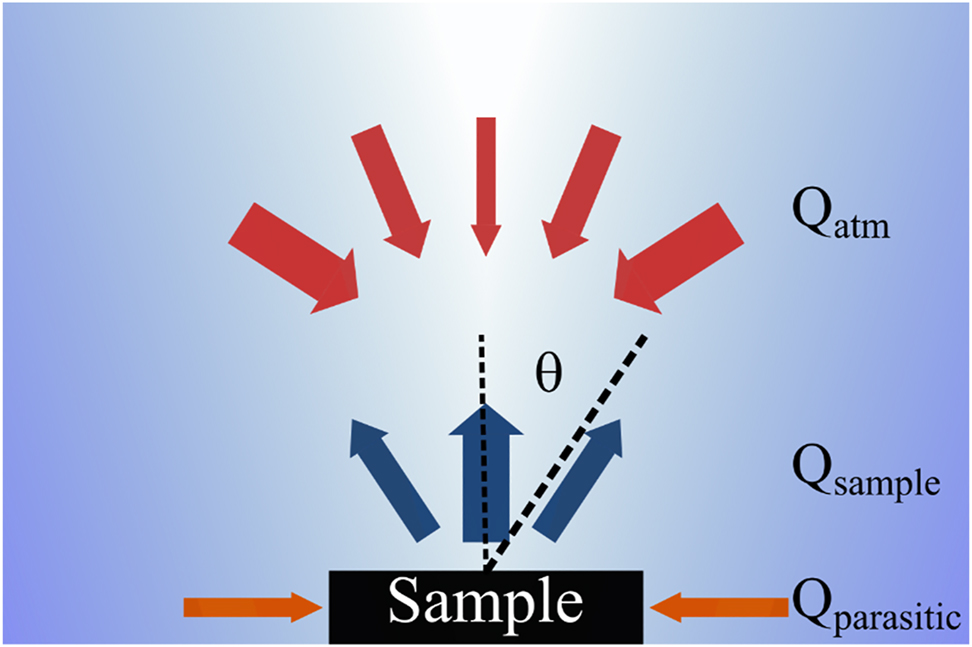
Radiative cooling (RC) is passive cooling strategy that cools without any electricity input could therefore have a significant impact on global energy consumption. This approach is particularly appealing to the community.
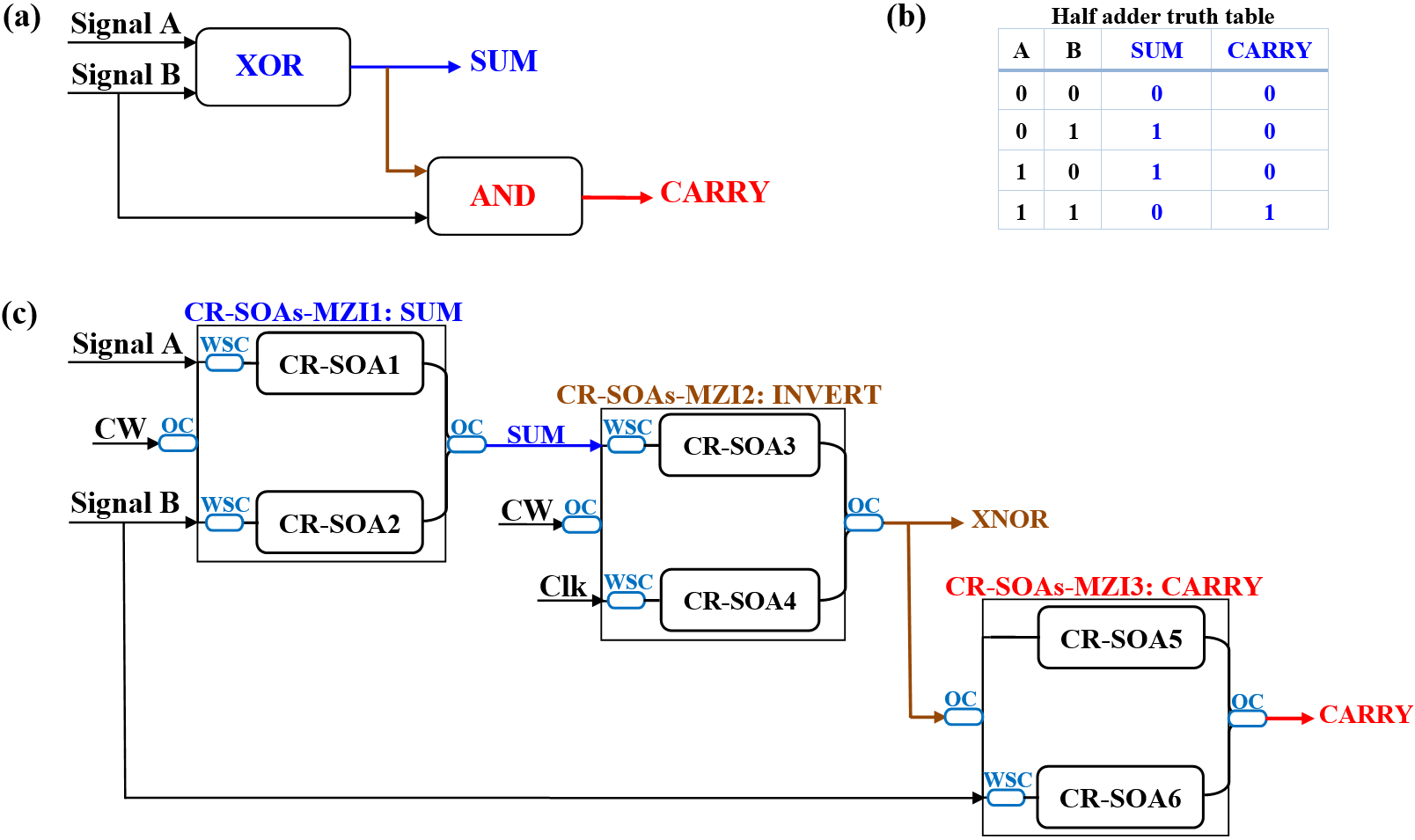
The half adder is a fundamental combinational circuit used in digital electronics that forms the foundation for more intricate processing circuits including full adders, binary decoders, binary counters, and shift registers.

Water is one of the Earth’s most abundant resources, 97% of it is saline that covers three-quarters of the Earth’s surface, and only 3% is freshwater, which is essential for daily human life. While expecting 2.5% is blocked in the polar ice caps, glaciers, and atmosphere, only 0.5% of water can be used for humans in the form of river water and groundwater
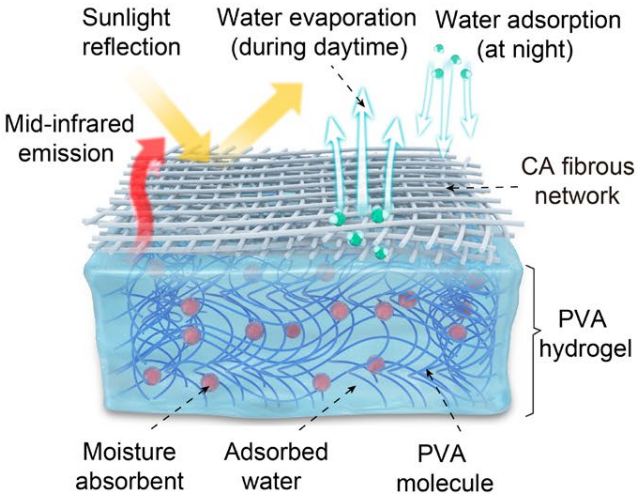
With the development of societies, cooling demand from buildings, electronic devices and power plants is huge and growing up. However, conventional cooling methods like air conditioning are high energy consumption. Radiative cooling and evaporative cooling with passive and low carbon footprints are considered to be promising strategies to retard energy scarcity and global warming.
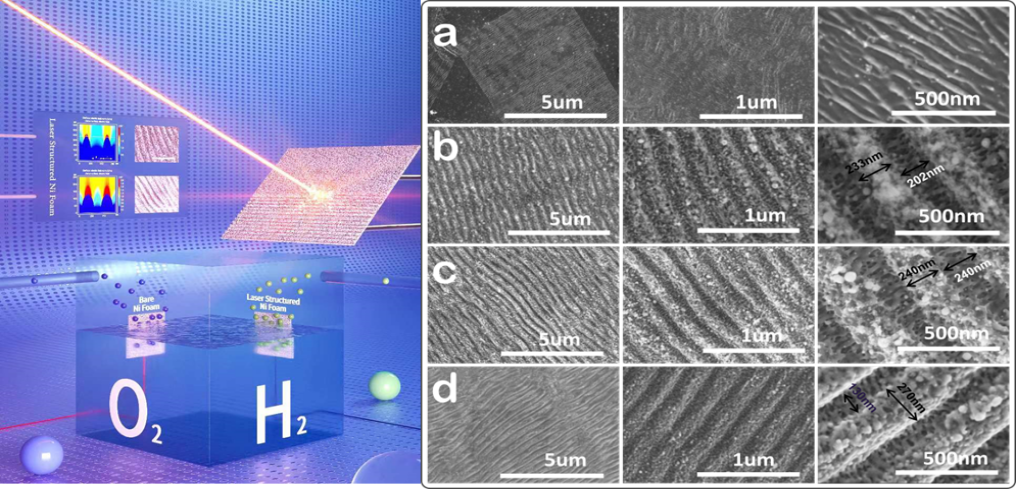
Hydrogen is produced by electrolysis and photolysis water splitting techniques with advantages for controlling energy resources, high energy density, ease of storage and transportation, and low pollution. The electrochemical process separates water into hydrogen and oxygen gases to store and transport to a fuel cell or combustion chamber; the by-products are mostly water.
