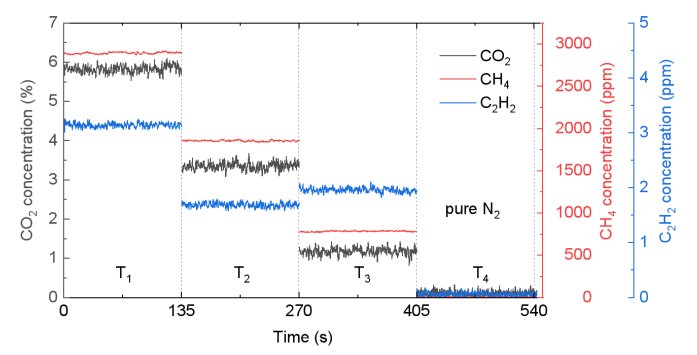
Trace gas detection based on laser absorption spectroscopy (LAS) is a powerful technique due to its high sensitivity and selectivity and is widely used in many fields. Most of current works are performed using a single frequency laser targeting only one species. Study on the interaction between different components needs simultaneous measurement of multi-species, which is still a challenge.
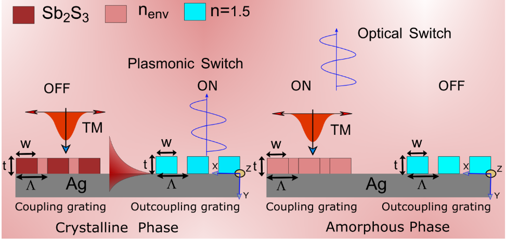
In order to integrate logic gates and communicate over short distances optically, plasmonic interconnections are essential components of optical interconnection schemes. Therefore, switching has attracted great attentions.
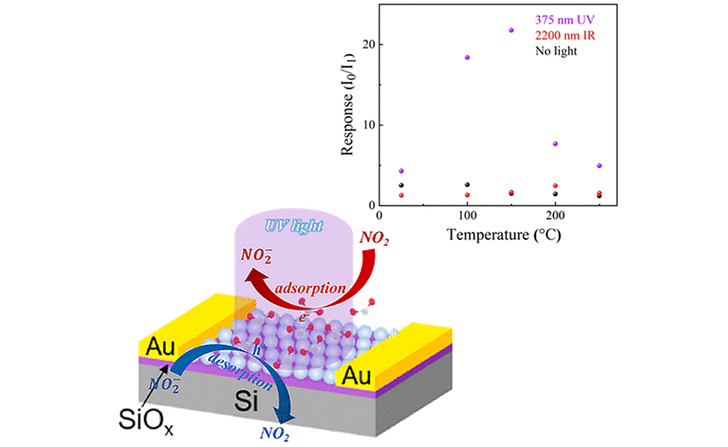
With the rapid development of portable devices and Internet of Things, the need for integration of sensors has accelerated the research of multifunctional sensing platforms. Multifunctional sensors that can detect light radiation, biological activities, stress, and gases in order to monitor environmental changes have great potential applications.
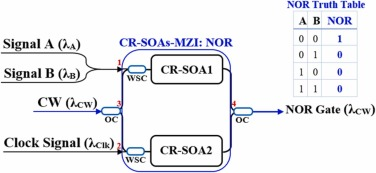
When an optical pulse train is delivered, two-photon absorption (TPA)-induced pumping causes considerable and quick gain and phase shifts in the carrier reservoir semiconductor optical amplifier (CR-SOA).
Renewable energy plays an important role for “Decarbonization and Net-zero Carbon Emission”. However, the integration difficulty of renewable energy technologies in harsh climatic areas limits its applications in high latitude areas.
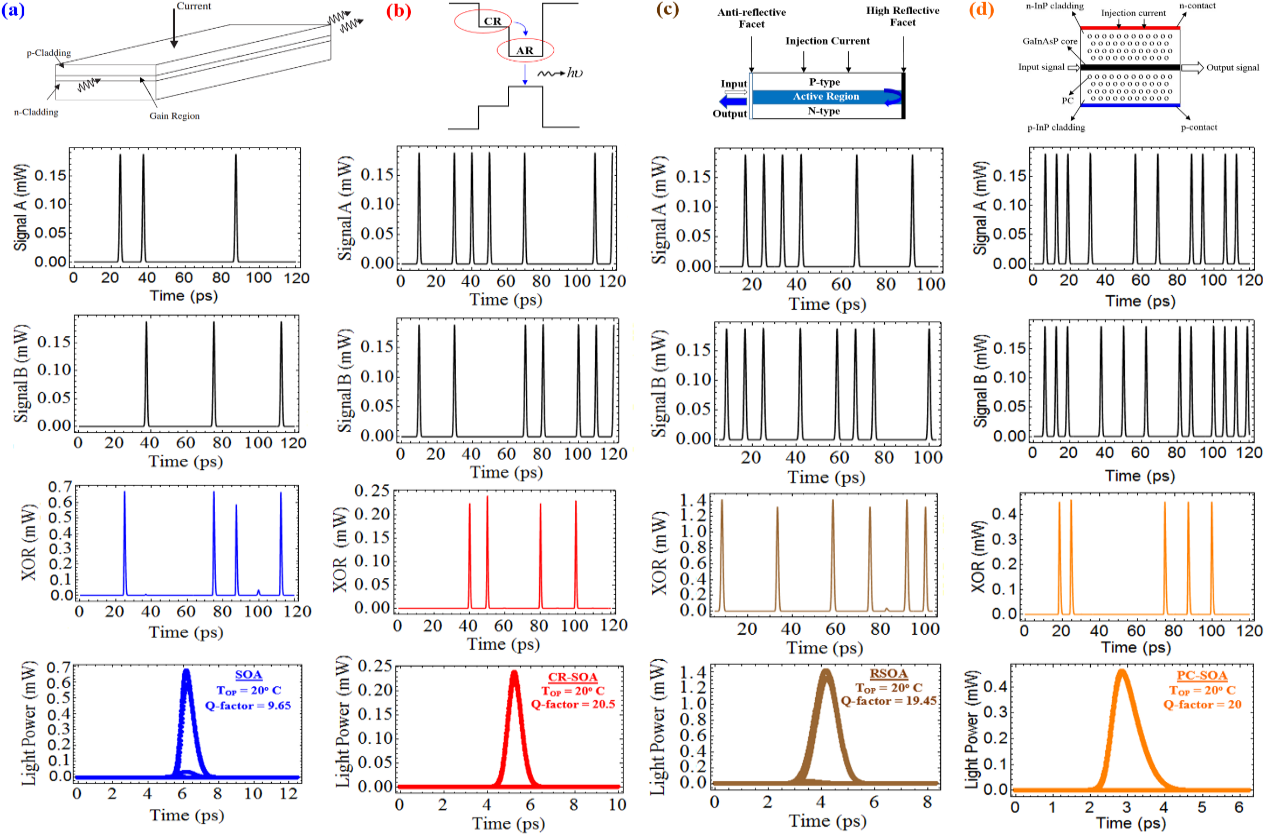
The effect of temperature on the performance of the semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs) is an important research point. Amer Kotb and his colleagues from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have for the first time investigated the effect of high temperatures on the performance of various SOAs.
