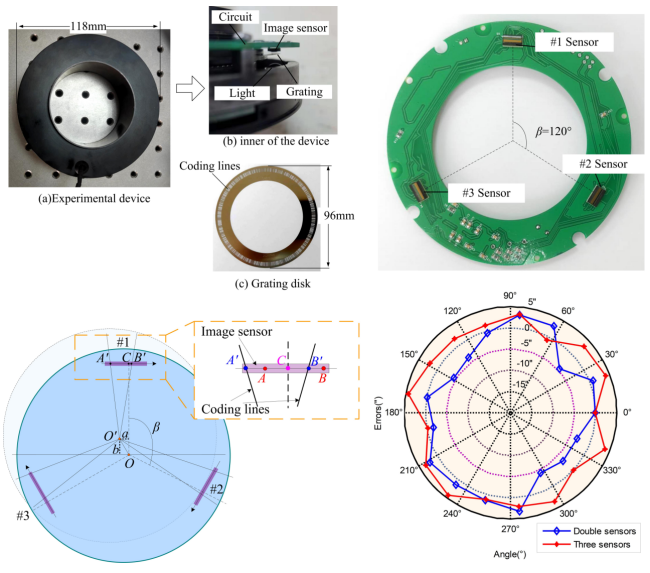
With the rapid development of numerical control technology in the industrial field, the accuracy of angular displacement measurement technology has become more demanding.
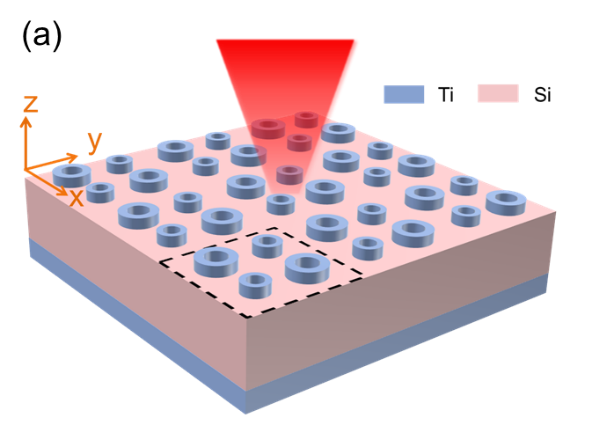
Metamaterial absorbers (MA) based on subwavelength periodic patterns can achieve perfect absorption at any target wavelength by rationally designing their geometric parameters. Due to their ultra-thin thickness and near-field enhancement, MAs are widely used in infrared imaging, thermal emitters, photodetection, solar energy harvesting, gas detection, etc. However, since the resonant nature of plasmon excitation, general MAs can only achieve perfect absorption in a narrow wavelength range.
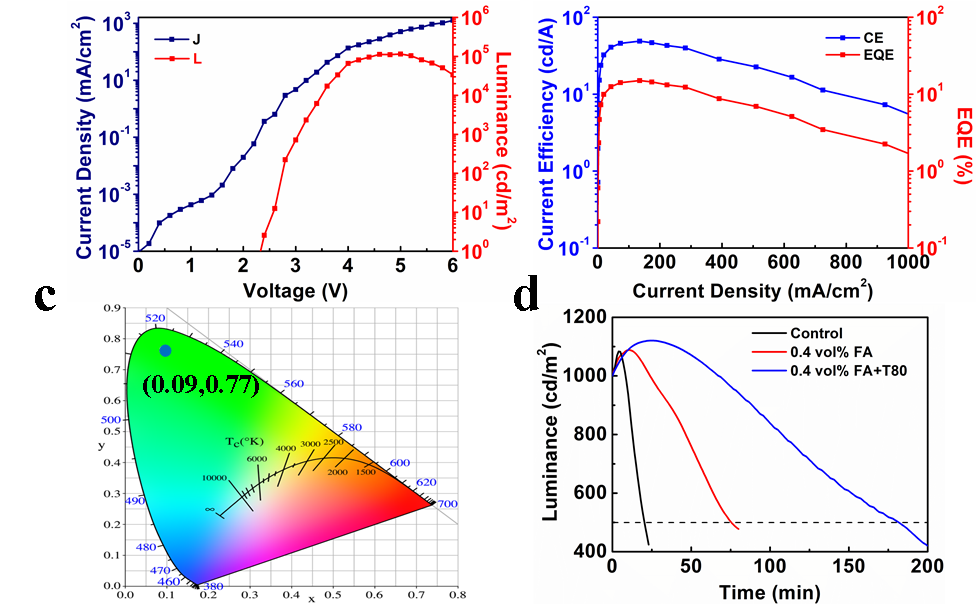
Metal halide perovskite material is a new type of photoelectric material with a range of advantages, such as high absorption coefficient, long carrier diffusion length, high mobility, and a tunable band gap. These advantages have made metal halide perovskite the spotlight in fields of solar cells, photodetectors, light-emitting diodes, and demonstration of lasers.
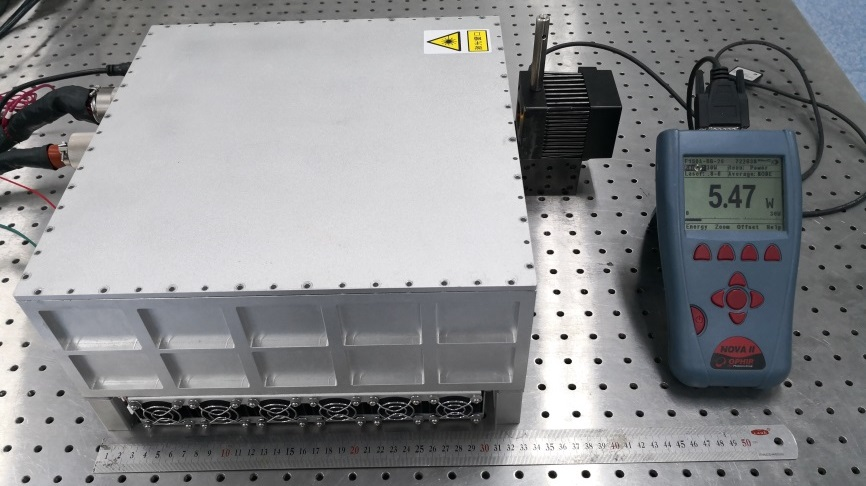

MgO-doped periodically poled lithium niobate (MgO:PPLN) optical parametric oscillators (OPOs) have the ability to generate high-power mid-infrared (MIR) laser with high efficiency. They have important applications in the fields of atmosphere monitoring, laser spectroscopy, photoelectric detection, and remote sensing surveys. In particular, miniaturized high-power MgO:PPLN OPOs are of paramount importance.
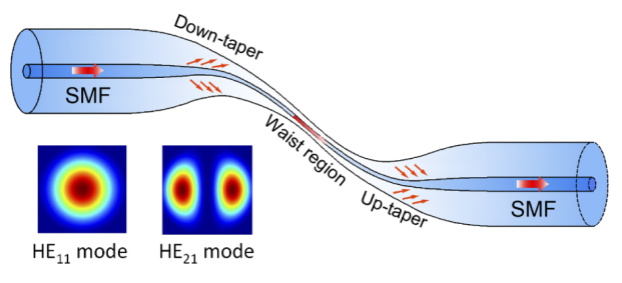
The dispersion turning point (DTP) in microfibers has proven to be an effective exceptional phenomenon for sensitivity improvement. In order to break the adiabaticity condition and excite higher-order modes effectively to satisfy the condition of DTP, the transition segments of tapered optical microfiber should be abrupt.
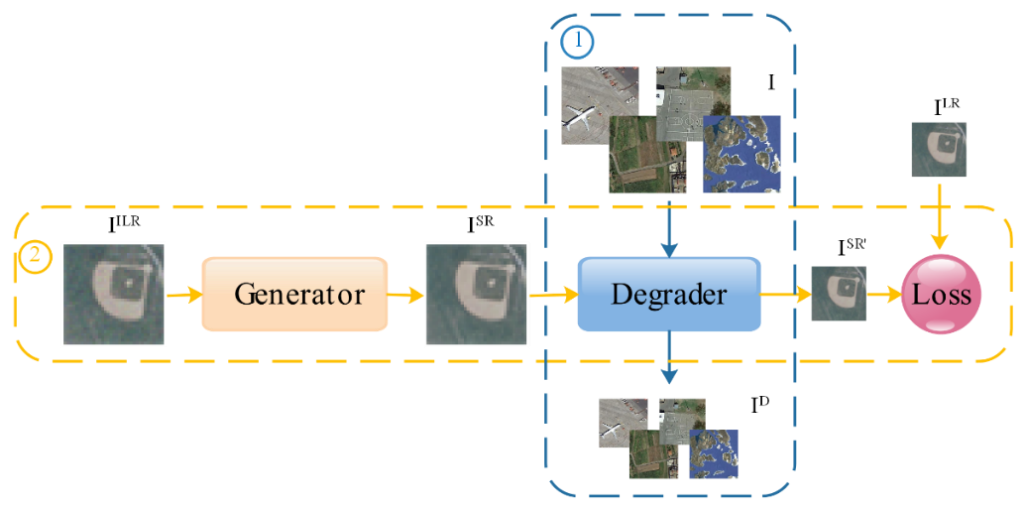
High resolution (HR) remote sensing images play an important role in environment monitoring, military reconnaissance, and urban planning. However, the direct acquisition of numerous HR images requires high-performance imaging equipment, while improving image resolution with super-resolution (SR) algorithm saves a lot in time and money. Therefore, it is of great significance to study on image SR algorithms.
