
The advantage of Two-photon pumped alkali vapor lasers (TPALs) is the realization of cascading and coaxial output of blue-violet photons and midinfrared photons, which can be used in many fields of military and scientific research, such as multi-wavelength detection, underwater communication, and photoelectric countermeasures.
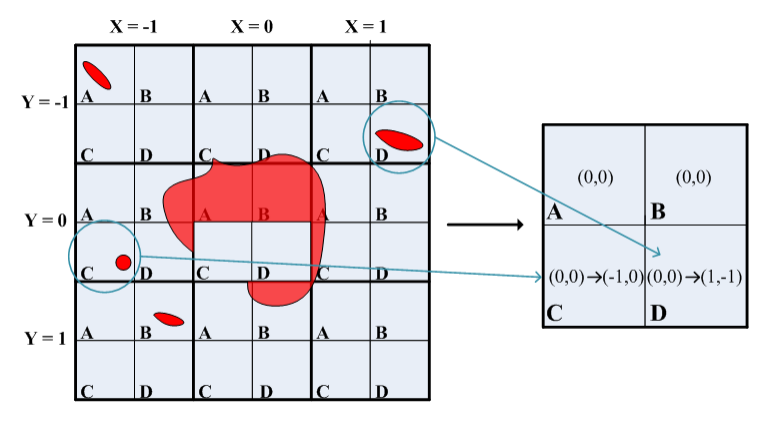
Wavefront reconstruction and correction under strong atmospheric turbulence conditions have become a crucial issue in adaptive optics. An approach based on plenoptic sensor can precisely reconstruct disturbed wavefront under strong atmospheric turbulence. However, the existing reconstruction algorithm has difficulty in reconstructing residual aberrations.
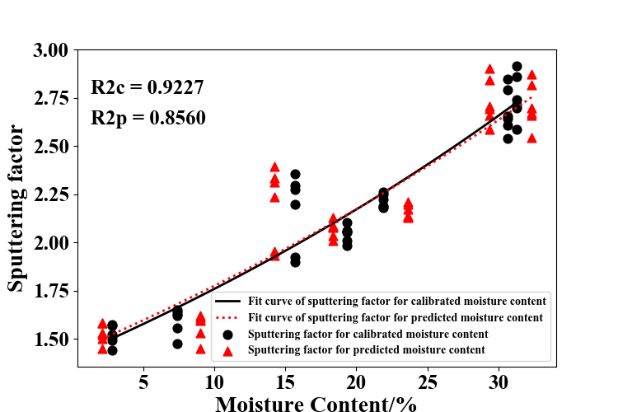
Fast on-site detection of potentially toxic metals in soils is crucial for soil remediation and contamination monitoring. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) technology has been used widely in soil remediation, food safety, biomedical analysis, and potentially toxic metal detection in crops. However, the detection of potentially toxic metals in soil by LIBS technology is currently performed in laboratory after drying
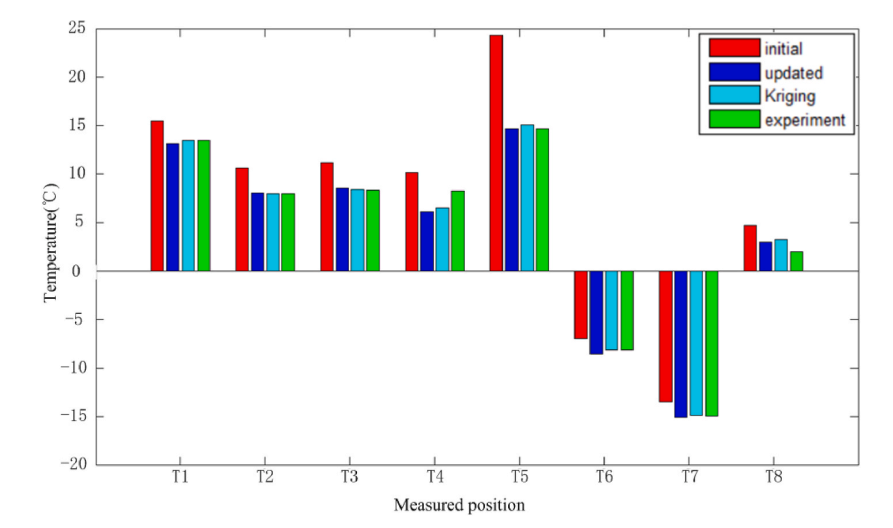
The thermal simulation analysis results are used to predict the temperature distribution of the spacecraft in orbit and guide the thermal design layout. Due to the complexity of aerospace instruments,too many thermal design parameters make it impossible to automatically modify the thermal models.
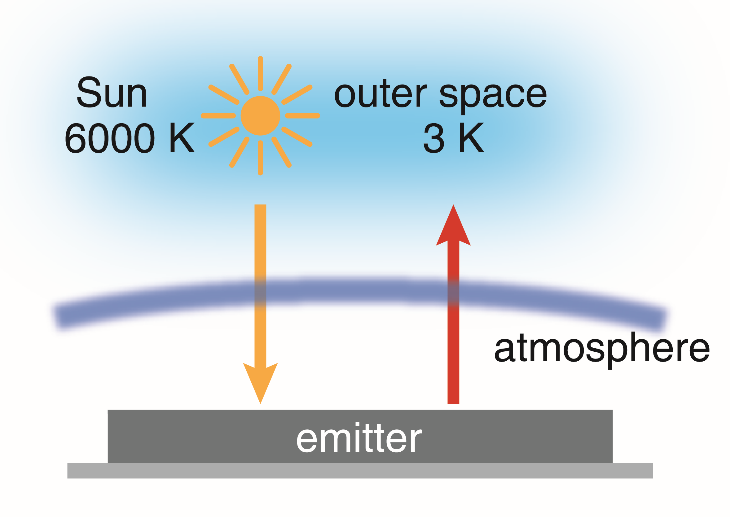
Radiative cooling is a ubiquitous passive cooling process that radiates heat out to the universe through the atmospheric transparency window. Recent advances in nanophotonics have enabled latest breakthroughs in daytime radiative cooling and have inspired intense research efforts in this field.
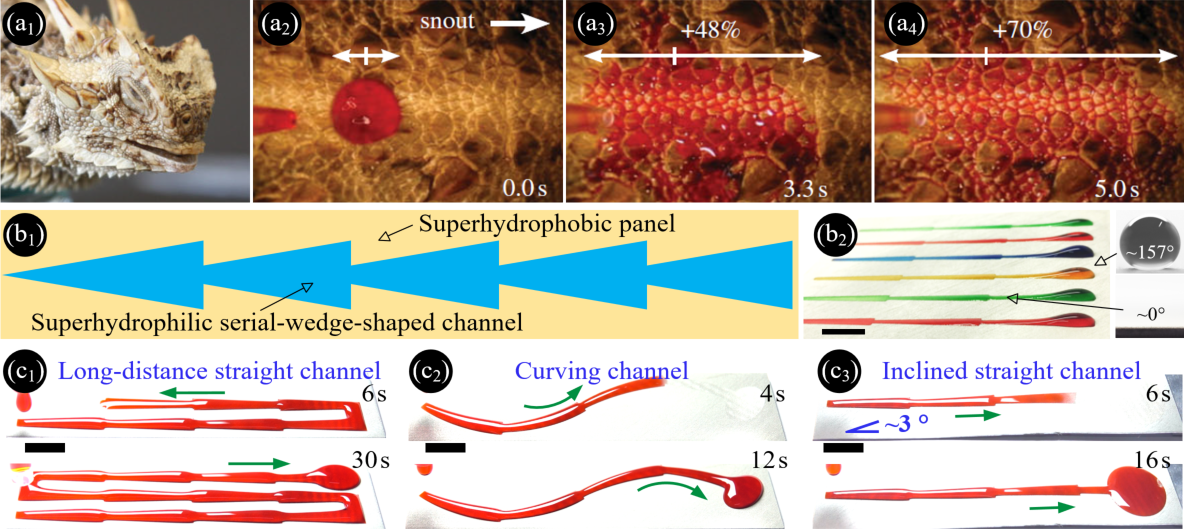
The Texas horned lizard (Iguanidae: Phrynosoma cornutum) inhabiting arid regions utilizes its dorsal integument to access water sources. Thanks to its highly-evolved integument consisting of microsized overlapping scales showing water repellency and nanosized capillary channels showing water affinity, water can be directed preferentially towards the lizard’s snout, achieving the power-free transportation.
