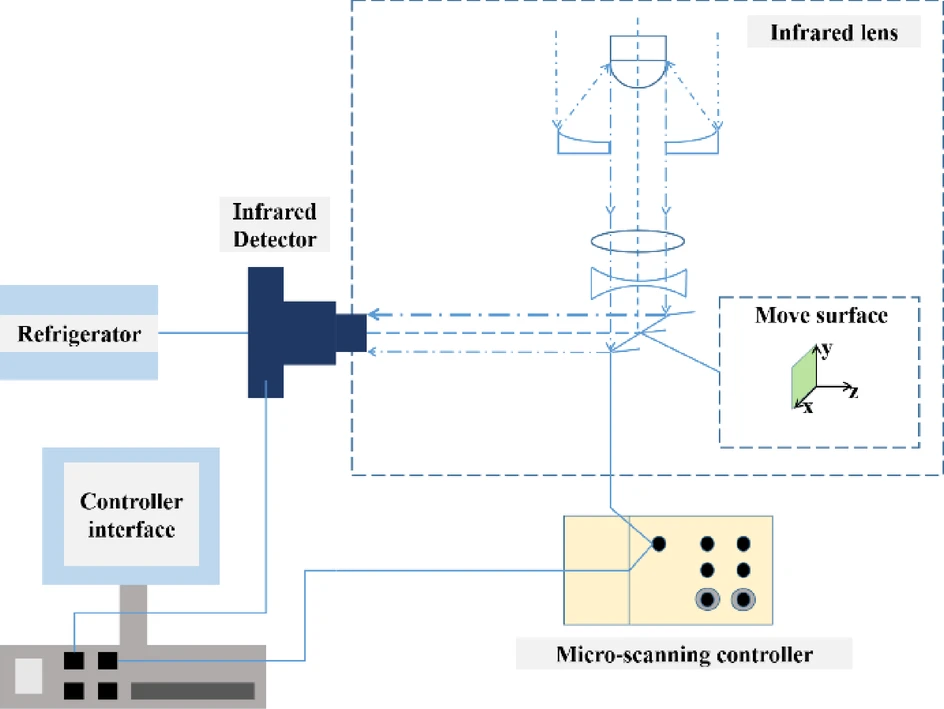
Researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, publishing in Scientific Reports, have created a new infrared imaging system that improves the clarity of dim, small targets often obscured by noise.
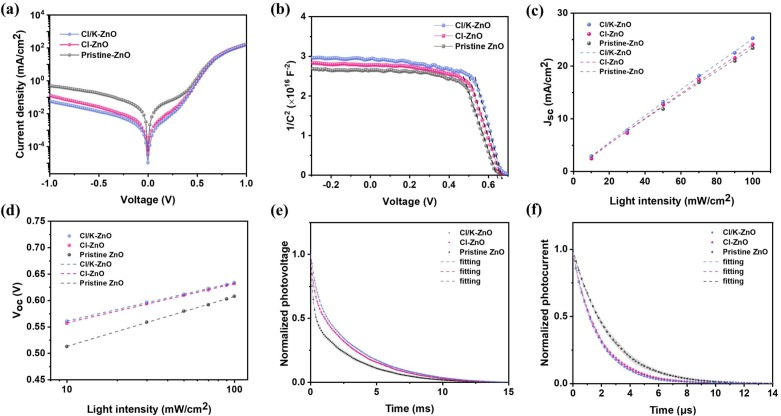
Researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Jingdezhen Ceramic University and Aalto University, have developed a surface engineering technique that significantly enhances the performance of quantum dot solar cells.
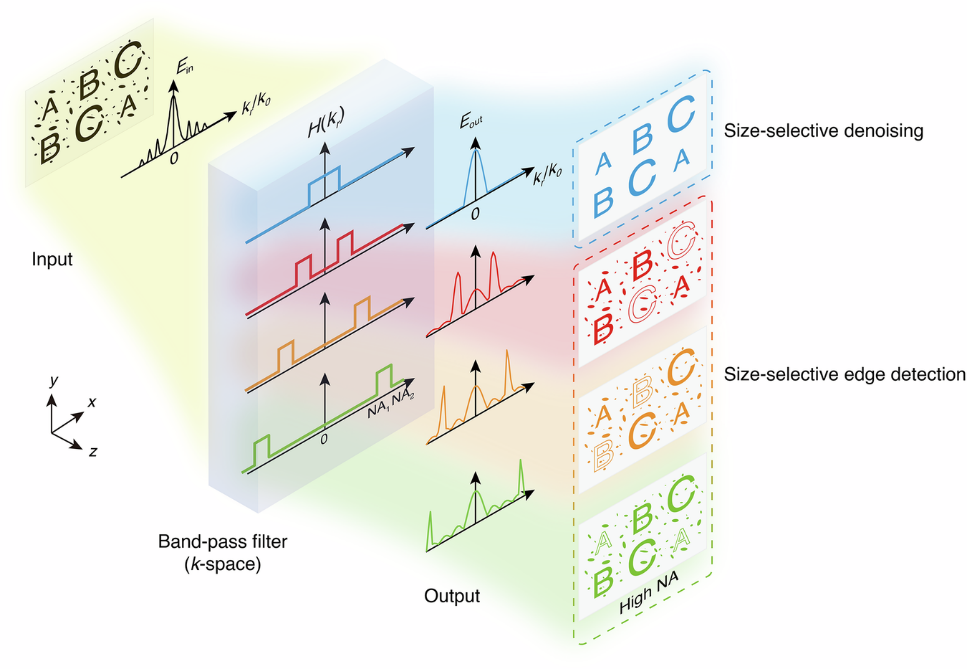
In the age of data-driven technologies, optical computing—which processes information using light instead of electricity—has emerged as a promising frontier. Unlike traditional electronic processors, optical systems can perform computations at the speed of light with extremely low energy consumption.
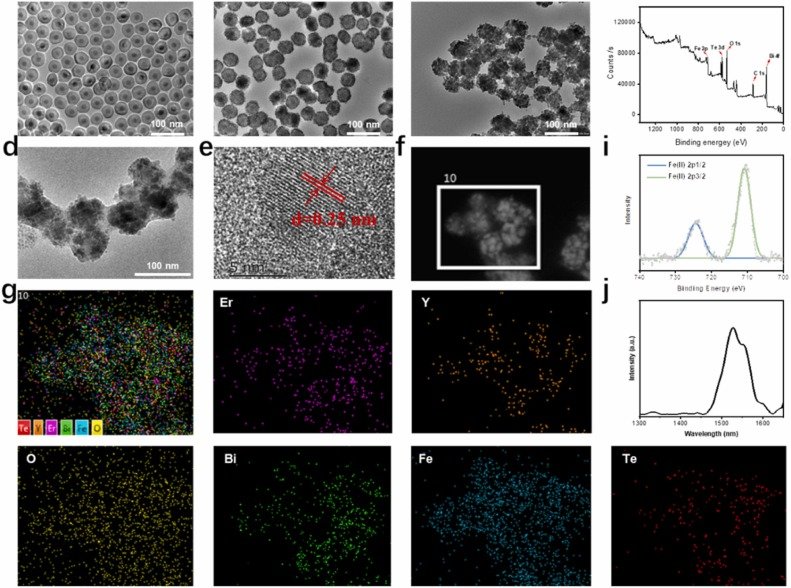
Researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, have developed a novel nanoplatform that integrates photothermal therapy (PTT), ferroptosis, and immunotherapy to combat tumors.
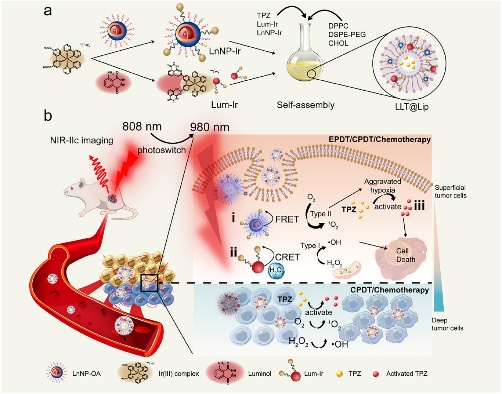
Researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a new nanoplatform that integrates dual-modality photodynamic therapy (PDT) and hypoxia-triggered chemotherapy, as reported in a recent study published in Small.
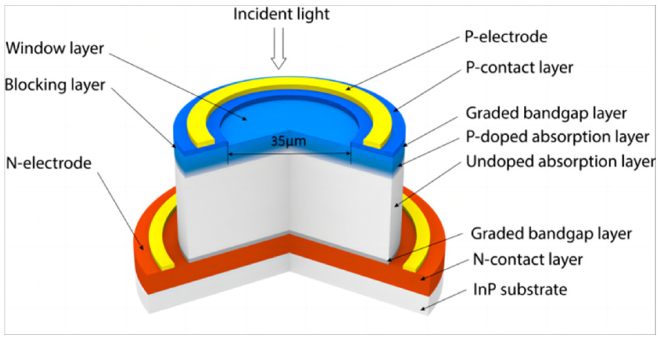
A recent study published in Sensors introduces a new high-speed, broadband photodiode that can detect wavelengths across the critical 850–1550 nm range. This research, developed by a team from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics, and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, marks a step forward for optical sensing and communication systems.
